biopipen.ns.scrna
Tools to analyze single-cell RNA
SeuratLoading(Proc) — Seurat - Loading data</>SeuratPreparing(Proc) — Load, prepare and apply QC to data, usingSeurat</>SeuratClustering(Proc) — Determine the clusters of cells without reference using Seurat FindClustersprocedure. </>SeuratSubClustering(Proc) — Find clusters of a subset of cells.</>SeuratClusterStats(Proc) — Statistics of the clustering.</>ModuleScoreCalculator(Proc) — Calculate the module scores for each cell</>CellsDistribution(Proc) — Distribution of cells (i.e. in a TCR clone) from different groupsfor each cluster </>SeuratMetadataMutater(Proc) — Mutate the metadata of the seurat object</>DimPlots(Proc) — Seurat - Dimensional reduction plots</>MarkersFinder(Proc) — Find markers between different groups of cells</>TopExpressingGenes(Proc) — Find the top expressing genes in each cluster</>ExprImputation(Proc) — This process imputes the dropout values in scRNA-seq data.</>SCImpute(Proc) — Impute the dropout values in scRNA-seq data.</>SeuratFilter(Proc) — Filtering cells from a seurat object</>SeuratSubset(Proc) — Subset a seurat object into multiple seruat objects</>SeuratSplit(Proc) — Split a seurat object into multiple seruat objects</>Subset10X(Proc) — Subset 10X data, mostly used for testing</>SeuratTo10X(Proc) — Write a Seurat object to 10X format</>ScFGSEA(Proc) — Gene set enrichment analysis for cells in different groups usingfgsea</>CellTypeAnnotation(Proc) — Annotate the cell clusters. Currently, four ways are supported:</>SeuratMap2Ref(Proc) — Map the seurat object to reference</>RadarPlots(Proc) — Radar plots for cell proportion in different clusters.</>MetaMarkers(Proc) — Find markers between three or more groups of cells, using one-way ANOVAor Kruskal-Wallis test. </>Seurat2AnnData(Proc) — Convert seurat object to AnnData</>AnnData2Seurat(Proc) — Convert AnnData to seurat object</>ScSimulation(Proc) — Simulate single-cell data using splatter.</>CellCellCommunication(Proc) — Cell-cell communication inference</>CellCellCommunicationPlots(Proc) — Visualization for cell-cell communication inference.</>ScVelo(Proc) — Velocity analysis for single-cell RNA-seq data</>Slingshot(Proc) — Trajectory inference using Slingshot</>LoomTo10X(Proc) — Convert Loom file to 10X format</>PseudoBulkDEG(Proc) — Pseduo-bulk differential gene expression analysis</>CellSNPLite(Proc) — Genotyping bi-allelic SNPs on single cells using cellsnp-lite.</>MQuad(Proc) — Clonal substructure discovery using single cell mitochondrial variants with MQuad.</>MQuadMerge(Proc) — Merge multiple MQuad results for multiple samples.</>VireoSNP(Proc) — Demultiplexing of single-cell RNA-seq data using vireoSNP.</>
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratLoading(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Seurat - Loading data
Deprecated, should be superseded by SeuratPreparing
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
metafile— The metadata of the samplesA tab-delimited file Two columns are required:- -
Sampleto specify the sample names. - -
RNADatato assign the path of the data to the samples
The path will be read byRead10X()fromSeurat
- -
rdsfile— The RDS file with a list of Seurat object
qc— The QC filter for each sample.This will be passed tosubset(obj, subset=<qc>). For examplenFeature_RNA > 200 & nFeature_RNA < 2500 & percent.mt < 5
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratPreparing(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Load, prepare and apply QC to data, using Seurat
This process will -
- - Prepare the seurat object
- - Apply QC to the data
- - Integrate the data from different samples
See also
- - https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/pbmc3k_tutorial.html#standard-pre-processing-workflow-1)
- - https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/integration_introduction
This process will read the scRNA-seq data, based on the information provided bySampleInfo, specifically, the paths specified by the RNAData column.
Those paths should be either paths to directoies containing matrix.mtx,
barcodes.tsv and features.tsv files that can be loaded by
Seurat::Read10X(),
or paths of loom files that can be loaded by SeuratDisk::LoadLoom(), or paths to
h5 files that can be loaded by
Seurat::Read10X_h5().
Each sample will be loaded individually and then merged into one Seurat object, and then perform QC.
In order to perform QC, some additional columns are added to the meta data of the Seurat object. They are:
precent.mt: The percentage of mitochondrial genes.percent.ribo: The percentage of ribosomal genes.precent.hb: The percentage of hemoglobin genes.percent.plat: The percentage of platelet genes.
For integration, two routes are available:
- Performing integration on datasets normalized with
SCTransform - Using
NormalizeDataandFindIntegrationAnchors
/// Note
When using SCTransform, the default Assay will be set to SCT in output, rather than RNA.
If you are using cca or rpca interation, the default assay will be integrated.
///
/// Note
From biopipen v0.23.0, this requires Seurat v5.0.0 or higher.
///
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
metafile— The metadata of the samplesA tab-delimited file Two columns are required:Sampleto specify the sample names.RNADatato assign the path of the data to the samples The path will be read byRead10X()fromSeurat, or the path to the h5 file that can be read byRead10X_h5()fromSeurat. It can also be an RDS or qs2 file containing aSeuratobject. Note that it must has a column namedSamplein the meta.data to specify the sample names.
outfile— The qs2 file with the Seurat object with all samples integrated.Note that the cell ids are prefixied with sample names.
DoubletFinder(ns) — Arguments to runDoubletFinder.See also https://demultiplexing-doublet-detecting-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/DoubletFinder.html.- - PCs (type=int): Number of PCs to use for 'doubletFinder' function.
- - doublets (type=float): Number of expected doublets as a proportion of the pool size.
- - pN (type=float): Number of doublets to simulate as a proportion of the pool size.
- - ncores (type=int): Number of cores to use for
DoubletFinder::paramSweep.
Set toNoneto useenvs.ncores.
Since parallelization of the function usually exhausts memory, if bigenvs.ncoresdoes not work
forDoubletFinder, set this to a smaller number.
FindVariableFeatures(ns) — Arguments forFindVariableFeatures().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with..IntegrateLayers(ns) — Arguments forIntegrateLayers().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with.. Whenuse_sctisTrue,normalization-methoddefaults toSCT.- - method (choice): The method to use for integration.
- CCAIntegration: UseSeurat::CCAIntegration.
- CCA: Same asCCAIntegration.
- cca: Same asCCAIntegration.
- RPCAIntegration: UseSeurat::RPCAIntegration.
- RPCA: Same asRPCAIntegration.
- rpca: Same asRPCAIntegration.
- HarmonyIntegration: UseSeurat::HarmonyIntegration.
- Harmony: Same asHarmonyIntegration.
- harmony: Same asHarmonyIntegration.
- FastMNNIntegration: UseSeurat::FastMNNIntegration.
- FastMNN: Same asFastMNNIntegration.
- fastmnn: Same asFastMNNIntegration.
- scVIIntegration: UseSeurat::scVIIntegration.
- scVI: Same asscVIIntegration.
- scvi: Same asscVIIntegration. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/integratelayers
- - method (choice): The method to use for integration.
NormalizeData(ns) — Arguments forNormalizeData().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with..RunPCA(ns) — Arguments forRunPCA().objectandfeaturesis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with..- - npcs (type=int): The number of PCs to compute.
For each sample,npcswill be no larger than the number of columns - 1. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/runpca
- - npcs (type=int): The number of PCs to compute.
SCTransform(ns) — Arguments forSCTransform().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with..- - return-only-var-genes: Whether to return only variable genes.
- - min_cells: The minimum number of cells that a gene must be expressed in to be kept.
A hidden argument ofSCTransformto filter genes.
If you try to keep all genes in theRNAassay, you can setmin_cellsto0and
return-only-var-genestoFalse.
See https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/issues/3598#issuecomment-715505537 - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/sctransform
ScaleData(ns) — Arguments forScaleData().objectandfeaturesis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with..cache(type=auto) — Whether to cache the information at different steps.IfTrue, the seurat object will be cached in the job output directory, which will be not cleaned up when job is rerunning. The cached seurat object will be saved as<signature>.<kind>.RDSfile, where<signature>is the signature determined by the input and envs of the process. See https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/issues/7849, https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/issues/5358 and https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/issues/6748 for more details also about reproducibility issues. To not use the cached seurat object, you can either setcachetoFalseor delete the cached file at<signature>.RDSin the cache directory.cell_qc— Filter expression to filter cells, usingtidyrseurat::filter(). It can also be a dictionary of expressions, where the names of the list are sample names. You can have a default expression in the list with the name "DEFAULT" for the samples that are not listed. Available QC keys includenFeature_RNA,nCount_RNA,percent.mt,percent.ribo,percent.hb, andpercent.plat.
/// Tip | Example Including the columns added above, all available QC keys includenFeature_RNA,nCount_RNA,percent.mt,percent.ribo,percent.hb, andpercent.plat. For example:
will keep cells with more than 200 genes and less than 5%% mitochondrial genes. ///[SeuratPreparing.envs] cell_qc = "nFeature_RNA > 200 & percent.mt < 5"doublet_detector(choice) — The doublet detector to use.- - none: Do not use any doublet detector.
- - DoubletFinder: Use
DoubletFinderto detect doublets. - - doubletfinder: Same as
DoubletFinder. - - scDblFinder: Use
scDblFinderto detect doublets. - - scdblfinder: Same as
scDblFinder.
gene_qc(ns) — Filter genes.gene_qcis applied aftercell_qc.- - min_cells: The minimum number of cells that a gene must be
expressed in to be kept. - - excludes: The genes to exclude. Multiple genes can be specified by
comma separated values, or as a list.
will keep genes that are expressed in at least 3 cells. ///[SeuratPreparing.envs] gene_qc = { min_cells = 3 }- - min_cells: The minimum number of cells that a gene must be
min_cells(type=int) — The minimum number of cells that a gene must beexpressed in to be kept. This is used inSeurat::CreateSeuratObject(). Futher QC (envs.cell_qc,envs.gene_qc) will be performed after this. It doesn't work when data is loaded from loom files or RDS/qs2 files.min_features(type=int) — The minimum number of features that a cell mustexpress to be kept. This is used inSeurat::CreateSeuratObject(). Futher QC (envs.cell_qc,envs.gene_qc) will be performed after this. It doesn't work when data is loaded from loom files or RDS/qs2 files.mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata to the cells.These new columns will be added to the metadata of the Seurat object and will be saved in the output file.ncores(type=int) — Number of cores to use.Used infuture::plan(strategy = "multicore", workers = <ncores>)to parallelize some Seurat procedures.no_integration(flag) — Whether to skip integration or not.qc_plots(type=json) — The plots for QC metrics.It should be a json (or python dict) with the keys as the names of the plots and the values also as dicts with the following keys:- * kind: The kind of QC. Either
geneorcell(default). - * devpars: The device parameters for the plot. A dict with
res,height, andwidth. - * more_formats: The formats to save the plots other than
png. - * save_code: Whether to save the code to reproduce the plot.
- * other arguments passed to
biopipen.utils::VizSeuratCellQCwhenkindiscellorbiopipen.utils::VizSeuratGeneQCwhenkindisgene.- * kind: The kind of QC. Either
scDblFinder(ns) — Arguments to runscDblFinder.- - dbr (type=float): The expected doublet rate.
- - ncores (type=int): Number of cores to use for
scDblFinder.
Set toNoneto useenvs.ncores. - -
: See https://rdrr.io/bioc/scDblFinder/man/scDblFinder.html.
use_sct(flag) — Whether use SCTransform routine to integrate samples or not.Before the following procedures, theRNAlayer will be split by samples.
IfFalse, following procedures will be performed in the order: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/seurat5_integration#layers-in-the-seurat-v5-objectand https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/pbmc3k_tutorial.html
IfTrue, following procedures will be performed in the order:- *
SCTransform.
- *
r-bracer—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(bracer)")
r-future—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(future)")
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(Seurat)")
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratClustering(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Determine the clusters of cells without reference using Seurat FindClustersprocedure.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
srtobj— The seurat object loaded by SeuratPreparing
outfile— The seurat object with cluster information atseurat_clustersorthe name specified byenvs.ident
FindClusters(ns) — Arguments forFindClusters().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with.. The cluster labels will be saved in cluster names and prefixed with "c". The first cluster will be "c1", instead of "c0".- - resolution (type=auto): The resolution of the clustering. You can have multiple resolutions as a list or as a string separated by comma.
Ranges are also supported, for example:0.1:0.5:0.1will generate0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5. The step can be omitted, defaulting to 0.1.
The results will be saved in<ident>_<resolution>.
The final resolution will be used to define the clusters at<ident>. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/findclusters
- - resolution (type=auto): The resolution of the clustering. You can have multiple resolutions as a list or as a string separated by comma.
FindNeighbors(ns) — Arguments forFindNeighbors().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with..- - reduction: The reduction to use.
If not provided,sobj@misc$integrated_new_reductionwill be used. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/findneighbors
- - reduction: The reduction to use.
RunPCA(ns) — Arguments forRunPCA().RunUMAP(ns) — Arguments forRunUMAP().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with..dims=Nwill be expanded todims=1:N; The maximal value ofNwill be the minimum ofNand the number of columns - 1 for each sample. You can also specifyfeaturesinstead ofdimsto use specific features for UMAP. It can be a list with the following fields:order(the order of the markers to use for UMAP, e.g. "desc(abs(avg_log2FC))", andn(the number of total features to use for UMAP, e.g. 30). Iffeaturesis a list, it will runbiopipen.utils::RunSeuratDEAnalysisto get the markers for each group, and then select the topn/ngroupsfeatures for each group based on theorderfield. Iffeaturesis a numeric value, it will be treated as thenfield in the list above, with the defaultorderbeing "desc(abs(avg_log2FC))".- - dims (type=int): The number of PCs to use
- - reduction: The reduction to use for UMAP.
If not provided,sobj@misc$integrated_new_reductionwill be used. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/runumap
cache(type=auto) — Where to cache the information at different steps.IfTrue, the seurat object will be cached in the job output directory, which will be not cleaned up when job is rerunning. Set toFalseto not cache the results.ident— The name in the metadata to save the cluster labels.A shortcut forenvs["FindClusters"]["cluster.name"].ncores(type=int;order=-100) — Number of cores to use.Used infuture::plan(strategy = "multicore", workers = <ncores>)to parallelize some Seurat procedures. See also: https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/future_vignette.html
r-dplyr—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(dplyr)")
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(Seurat)")
r-tidyr—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(tidyr)")
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratSubClustering(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Find clusters of a subset of cells.
It's unlike [Seurat::FindSubCluster], which only finds subclusters of a single
cluster. Instead, it will perform the whole clustering procedure on the subset of
cells. One can use metadata to specify the subset of cells to perform clustering on.
For the subset of cells, the reductions will be re-performed on the subset of cells,
and then the clustering will be performed on the subset of cells. The reduction
will be saved in object@reduction$<casename>.<reduction> of the original object and the
clustering will be saved in the metadata of the original object using the casename
as the column name.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
srtobj— The seurat object in RDS or qs/qs2 format.
outfile— The seurat object with the subclustering information in qs/qs2 format.
FindClusters(ns) — Arguments forFindClusters().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with.. The cluster labels will be prefixed with "s". The first cluster will be "s1", instead of "s0".- - resolution (type=auto): The resolution of the clustering. You can have multiple resolutions as a list or as a string separated by comma.
Ranges are also supported, for example:0.1:0.5:0.1will generate0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5. The step can be omitted, defaulting to 0.1.
The results will be saved in<casename>_<resolution>.
The final resolution will be used to define the clusters at<casename>. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/findclusters
- - resolution (type=auto): The resolution of the clustering. You can have multiple resolutions as a list or as a string separated by comma.
FindNeighbors(ns) — Arguments forFindNeighbors().objectis specified internally, and-in the key will be replaced with..- - reduction: The reduction to use.
If not provided,object@misc$integrated_new_reductionwill be used. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/findneighbors
- - reduction: The reduction to use.
RunPCA(ns) — Arguments forRunPCA().objectis specified internally as the subset object, and-in the key will be replaced with..RunUMAP(ns) — Arguments forRunUMAP().objectis specified internally as the subset object, and-in the key will be replaced with..dims=Nwill be expanded todims=1:N; The maximal value ofNwill be the minimum ofNand the number of columns - 1 for each sample. You can also specifyfeaturesinstead ofdimsto use specific features for UMAP. It can be a list with the following fields:order(the order of the markers to use for UMAP, e.g. "desc(abs(avg_log2FC))", andn(the number of total features to use for UMAP, e.g. 30). Iffeaturesis a list, it will runbiopipen.utils::RunSeuratDEAnalysisto get the markers for each group, and then select the topn/ngroupsfeatures for each group based on theorderfield. Iffeaturesis a numeric value, it will be treated as thenfield in the list above, with the defaultorderbeing "desc(abs(avg_log2FC))".- - dims (type=int): The number of PCs to use
- - reduction: The reduction to use for UMAP.
If not provided,sobj@misc$integrated_new_reductionwill be used. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/runumap
cache(type=auto) — Whether to cache the results.IfTrue, the seurat object will be cached in the job output directory, which will be not cleaned up when job is rerunning. Set toFalseto not cache the results.cases(type=json) — The cases to perform subclustering.Keys are the names of the cases and values are the dicts inherited fromenvsexceptmutatersandcache. If empty, a case with namesubclusterwill be created with default parameters. The case name will be passed tobiopipen.utils::SeuratSubCluster()asname. It will be used as the prefix for the reduction name, keys and cluster names. For reduction keys, it will betoupper(<name>)+ "PC_" andtoupper(<name>)+ "UMAP_". For cluster names, it will be<name>+ "." + resolution. And the final cluster name will be<name>. Note that thenameshould be alphanumeric and anything other than alphanumeric will be removed.mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata to subset the cells.The mutaters will be applied in the order specified.ncores(type=int;order=-100) — Number of cores to use.Used infuture::plan(strategy = "multicore", workers = <ncores>)to parallelize some Seurat procedures.subset— An expression to subset the cells, will be passed totidyseurat::filter().
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratClusterStats(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Statistics of the clustering.
Including the number/fraction of cells in each cluster, the gene expression values and dimension reduction plots. It's also possible to perform stats on TCR clones/clusters or other metadata for each T-cell cluster.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
Clustree Plot
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.clustrees."Clustree Plot"]
prefix = "seurat_clusters"
devpars = {height = 500}
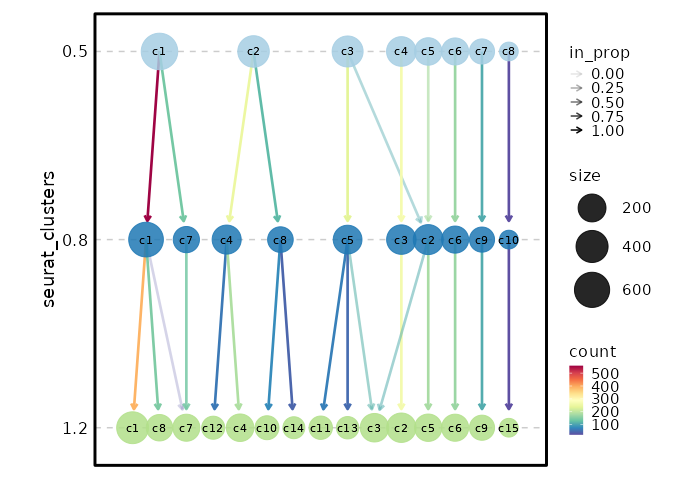 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Number of cells in each cluster (Bar Chart)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.stats."Number of cells in each cluster (Bar Chart)"]
plot_type = "bar"
x_text_angle = 90
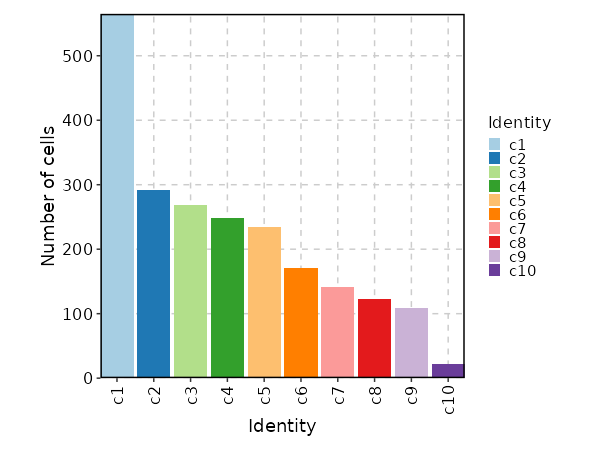 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Number of cells in each cluster by Sample (Bar Chart)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.stats."Number of cells in each cluster by Sample (Bar Chart)"]
plot_type = "bar"
group_by = "Sample"
x_text_angle = 90
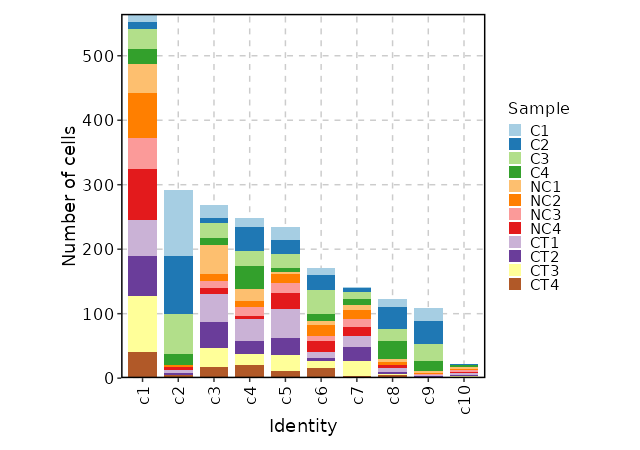 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Number of cells in each cluster by Diagnosis
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.stats."Number of cells in each cluster by Diagnosis"]
plot_type = "bar"
group_by = "Diagnosis"
frac = "group"
x_text_angle = 90
swap = true
position = "stack"
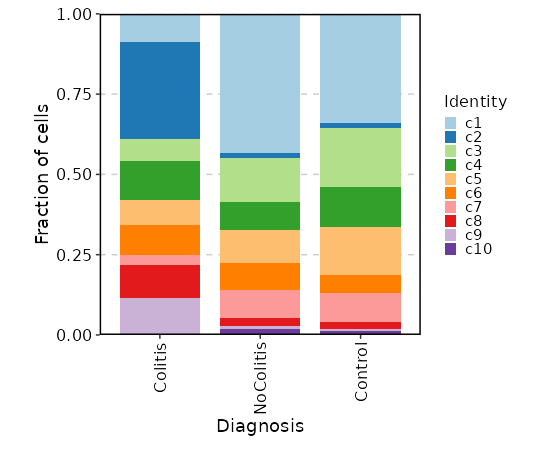 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Number of cells in each cluster by Diagnosis (Circos Plot)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.stats."Number of cells in each cluster by Diagnosis (Circos Plot)"]
plot_type = "circos"
group_by = "Diagnosis"
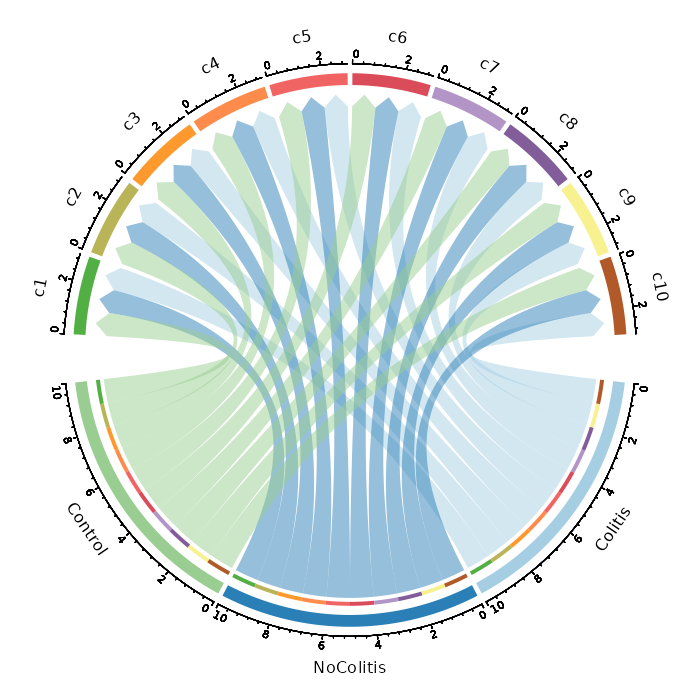 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Number of cells in each cluster by Diagnosis (Sankey Plot)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.stats."Number of cells in each cluster by Diagnosis (Sankey Plot)"]
plot_type = "sankey"
group_by = ["seurat_clusters", "Diagnosis"]
links_alpha = 0.6
devpars = {width = 800}
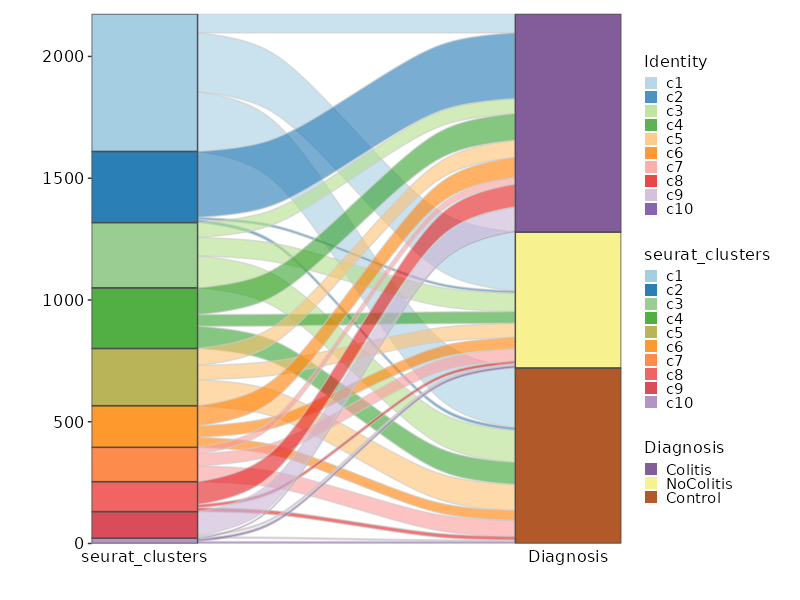 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Number of cells in each cluster by Sample (Spider Plot)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.stats."Number of cells in each cluster by Sample (Spider Plot)"]
plot_type = "spider"
group_by = "Diagnosis"
palette = "Set1"
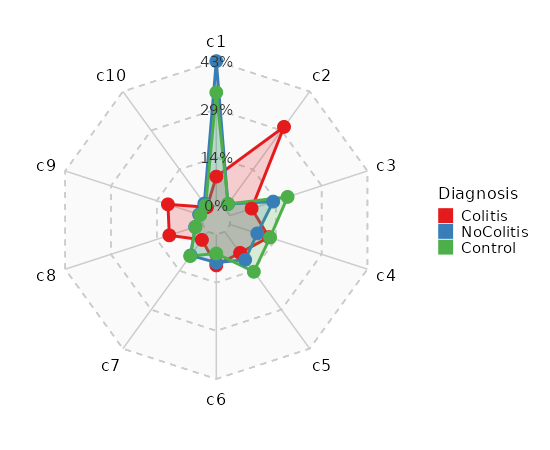 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Number of genes detected in each cluster
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.ngenes."Number of genes detected in each cluster"]
plot_type = "violin"
add_box = true
add_point = true
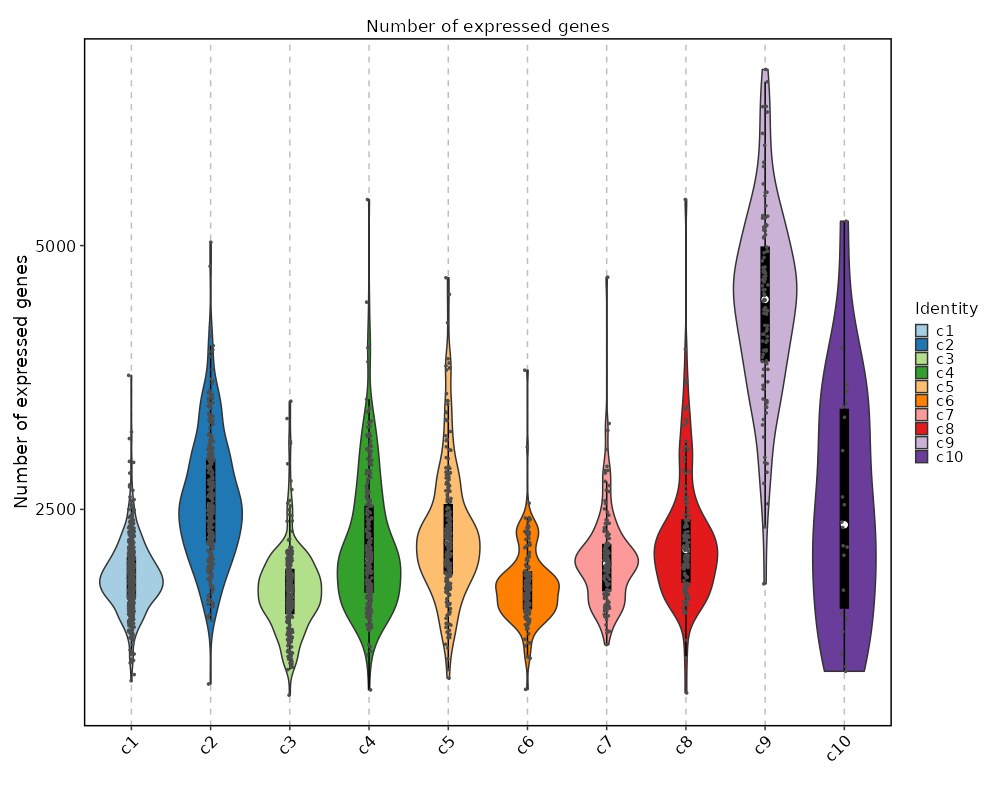 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Feature Expression in Clusters (Violin Plots)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features_defaults]
features = ["CD3D", "CD4", "CD8A", "MS4A1", "CD14", "LYZ", "FCGR3A", "NCAM1", "KLRD1"]
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features."Feature Expression in Clusters (Violin Plots)"]
plot_type = "violin"
ident = "seurat_clusters"
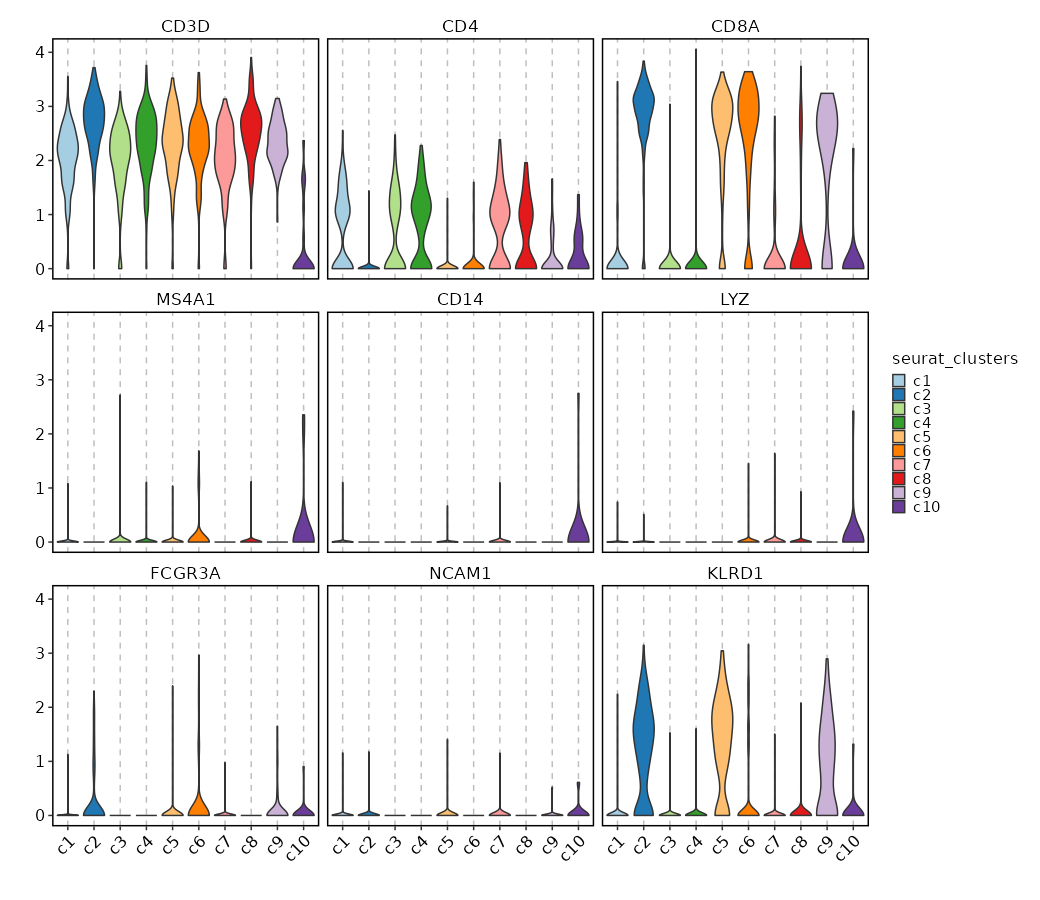 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Feature Expression in Clusters (Ridge Plots)
# Using the same features as above
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features."Feature Expression in Clusters (Ridge Plots)"]
plot_type = "ridge"
ident = "seurat_clusters"
flip = true
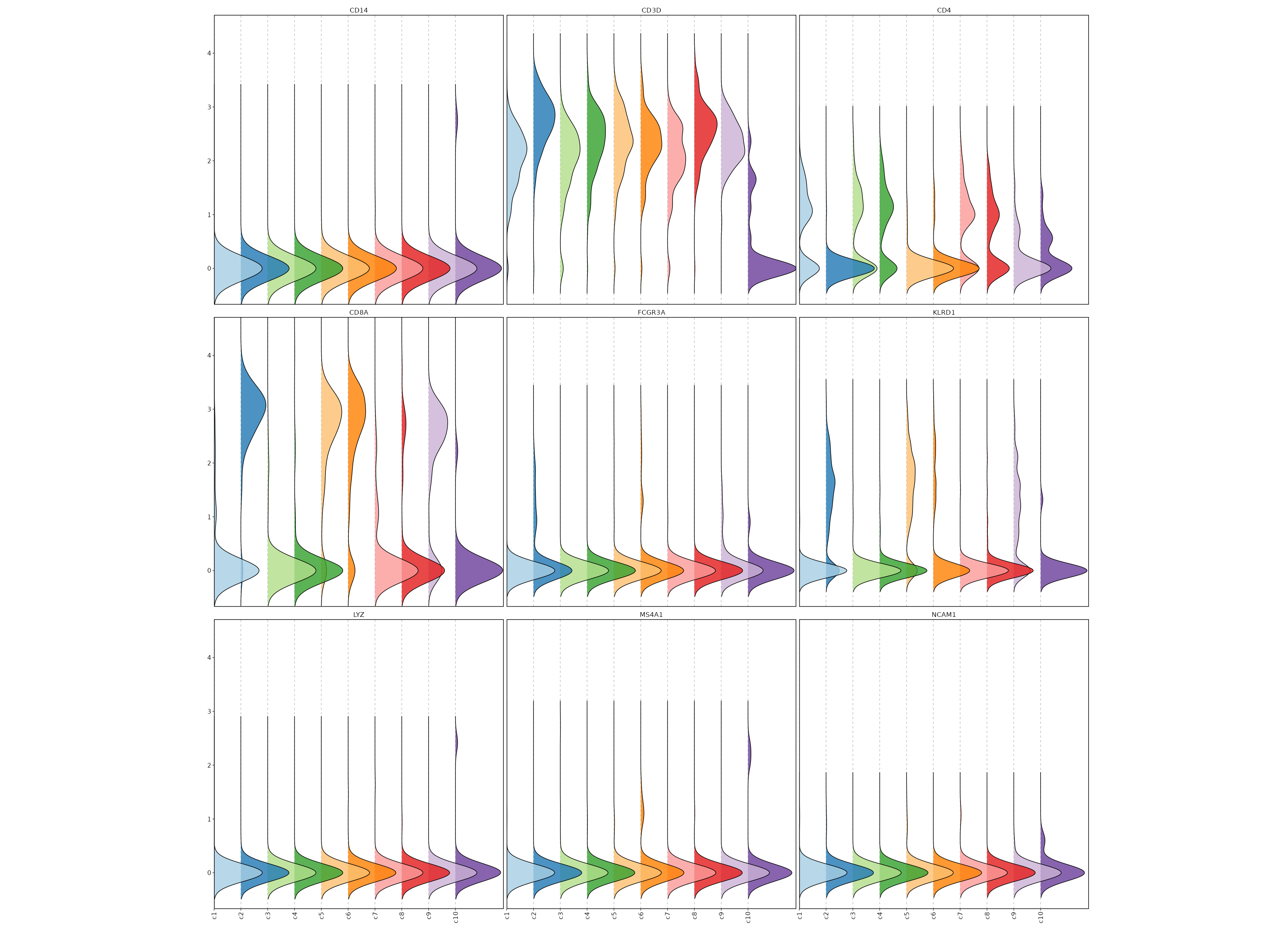 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Feature Expression in Clusters by Diagnosis
# Using the same features as above
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features."Feature Expression in Clusters by Diagnosis"]
plot_type = "violin"
group_by = "Diagnosis"
ident = "seurat_clusters"
comparisons = true
sig_label = "p.signif"
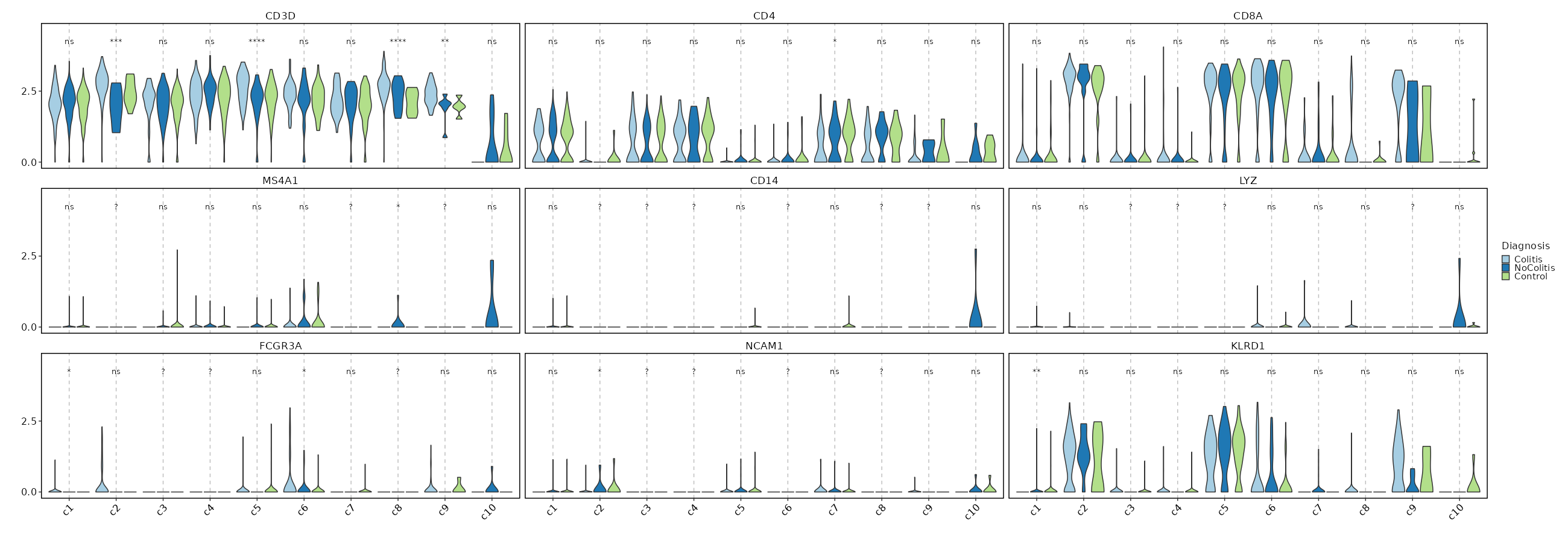 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Feature Expression in Clusters (stacked)
# Using the same features as above
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features."Feature Expression in Clusters (stacked)"]
plot_type = "violin"
ident = "seurat_clusters"
add_bg = true
stack = true
add_box = true
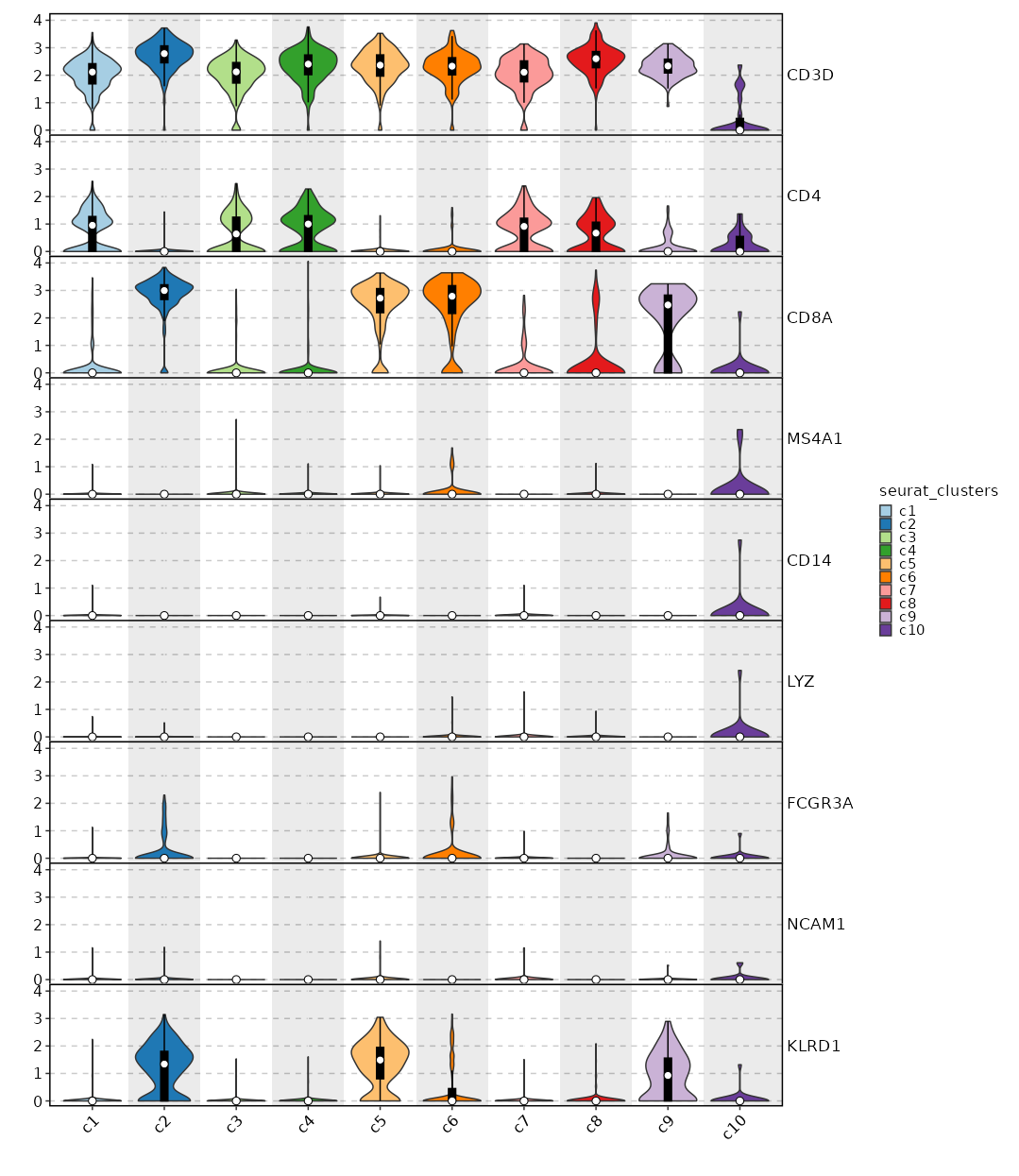 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
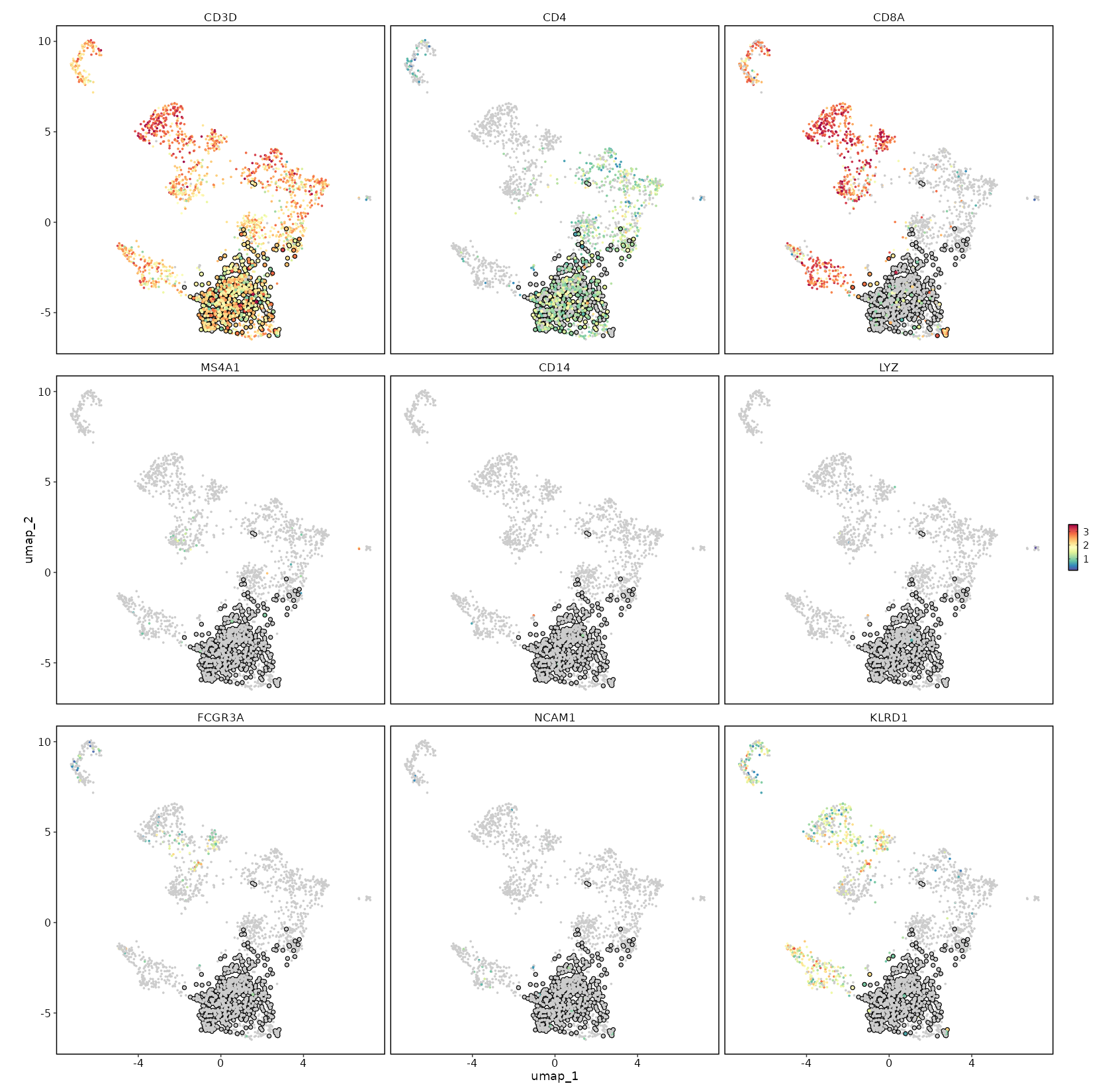
CD4 Expression on UMAP
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features."CD4 Expression on UMAP"]
plot_type = "dim"
feature = "CD4"
highlight = "seurat_clusters == 'c1'"
 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
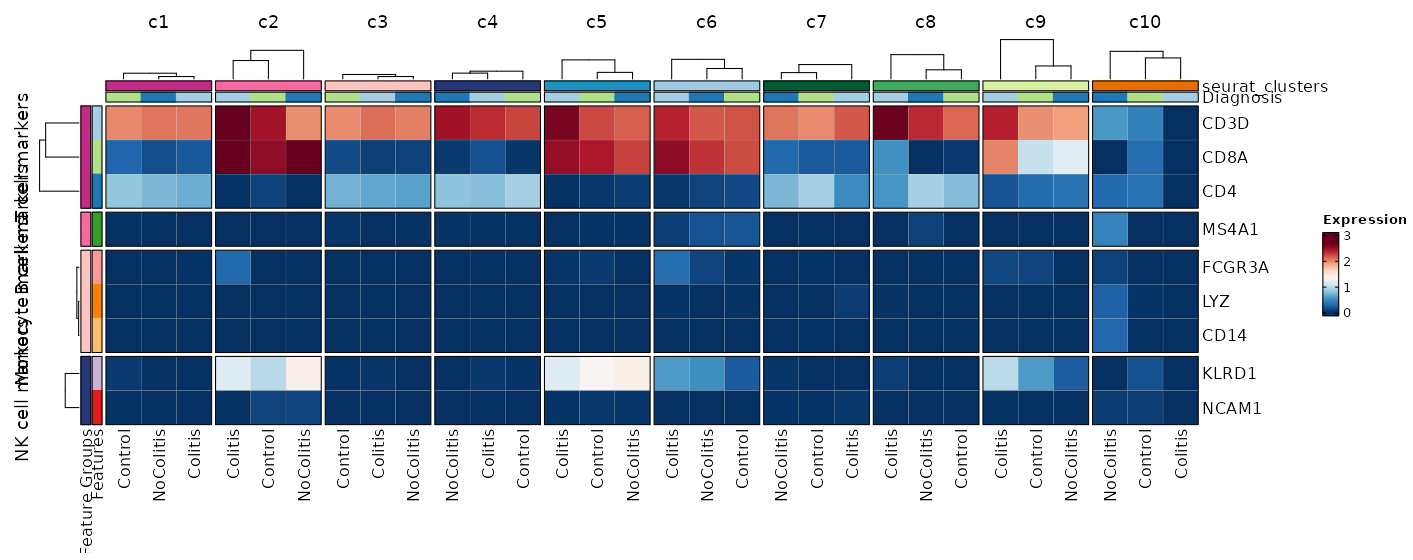
Feature Expression in Clusters by Diagnosis (Heatmap)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features."Feature Expression in Clusters by Diagnosis (Heatmap)"]
# Grouped features
features = {"T cell markers" = ["CD3D", "CD4", "CD8A"], "B cell markers" = ["MS4A1"], "Monocyte markers" = ["CD14", "LYZ", "FCGR3A"], "NK cell markers" = ["NCAM1", "KLRD1"]}
plot_type = "heatmap"
ident = "Diagnosis"
columns_split_by = "seurat_clusters"
name = "Expression"
devpars = {height = 560}
 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
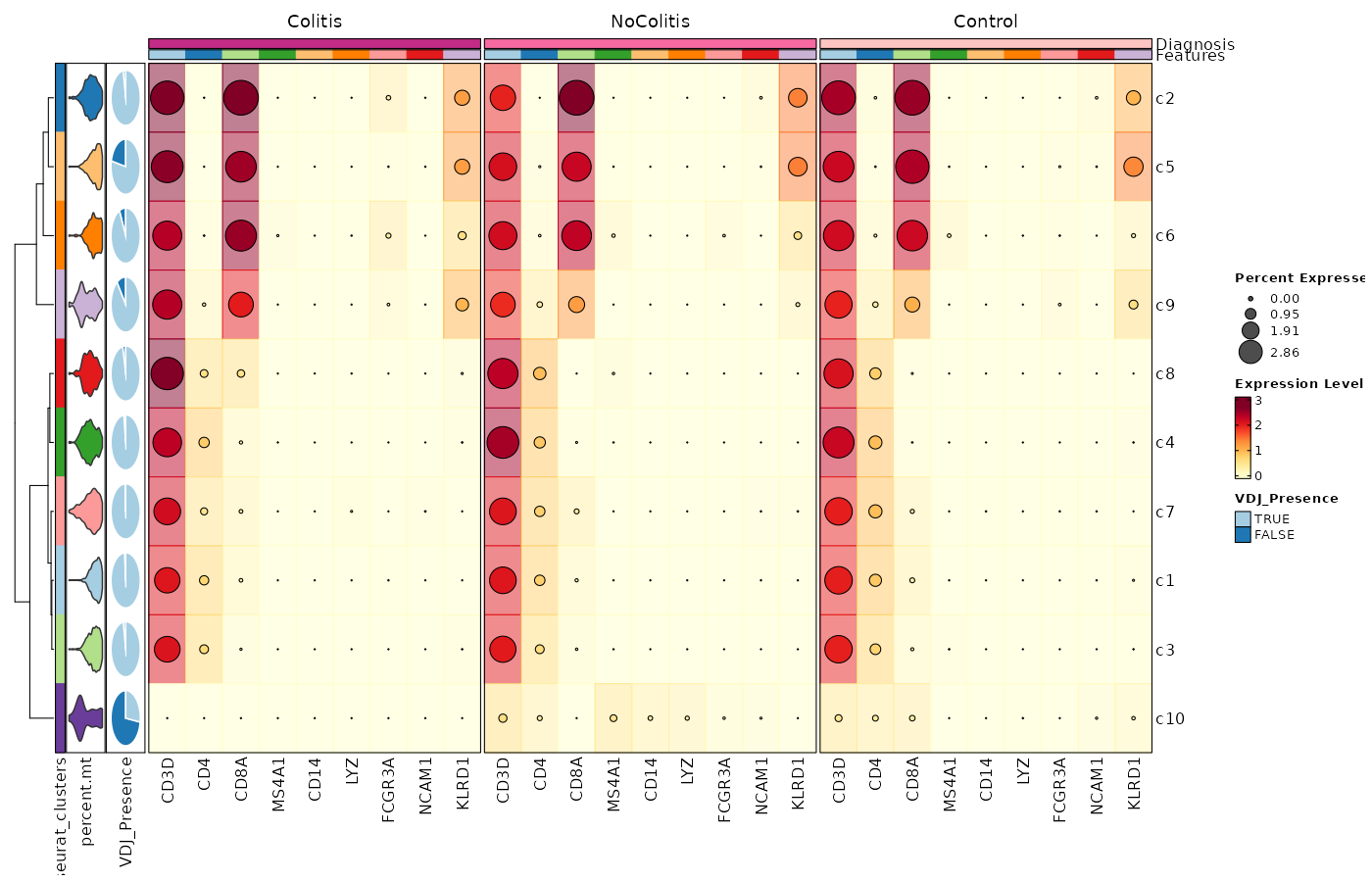
Feature Expression in Clusters by Diagnosis (Heatmap with annotations)
# Using the default features
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features."Feature Expression in Clusters by Diagnosis (Heatmap with annotations)"]
ident = "seurat_clusters"
cell_type = "dot"
plot_type = "heatmap"
name = "Expression Level"
dot_size = "nanmean"
dot_size_name = "Percent Expressed"
add_bg = true
rows_split_by = "Diagnosis"
cluster_rows = false
flip = true
palette = "YlOrRd"
column_annotation = ["percent.mt", "VDJ_Presence"]
column_annotation_type = {"percent.mt" = "violin", VDJ_Presence = "pie"}
column_annotation_params = {"percent.mt" = {show_legend = false}}
devpars = {width = 1400, height = 900}
 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
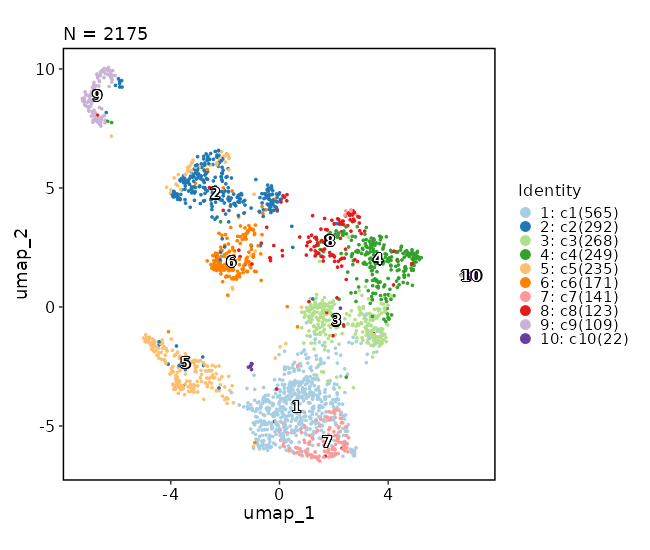
Dimensional reduction plot
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.features."Dimensional reduction plot"]
label = true
 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Dimensional reduction plot (with marks)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.dimplots."Dimensional reduction plot (with marks)"]
add_mark = true
mark_linetype = 2
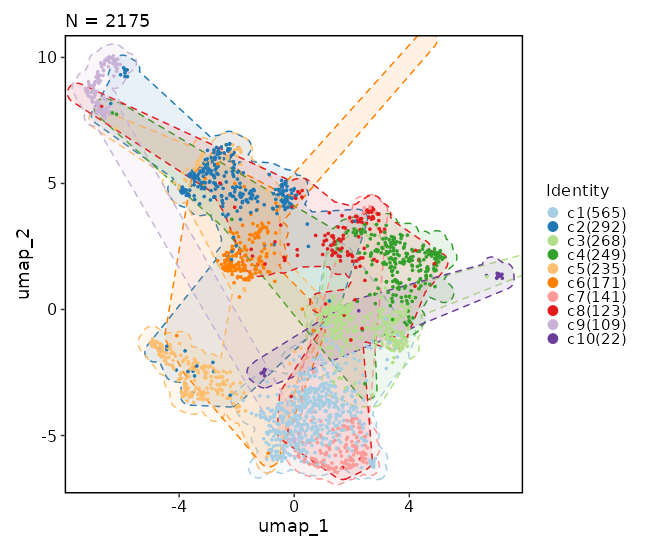 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Dimensional reduction plot (with hex bins)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.dimplots."Dimensional reduction plot (with hex bins)"]
hex = true
hex_bins = 50
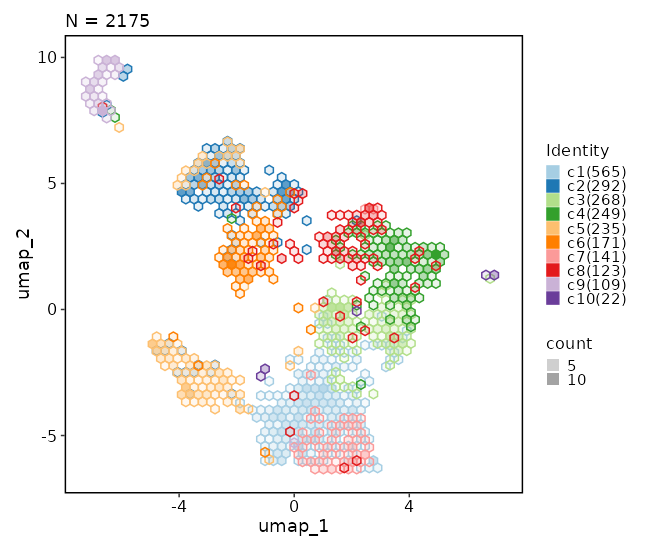 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Dimensional reduction plot (with Diagnosis stats)
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.dimplots."Dimensional reduction plot (with Diagnosis stats)"]
stat_by = "Diagnosis"
stat_plot_type = "ring"
stat_plot_size = 0.15
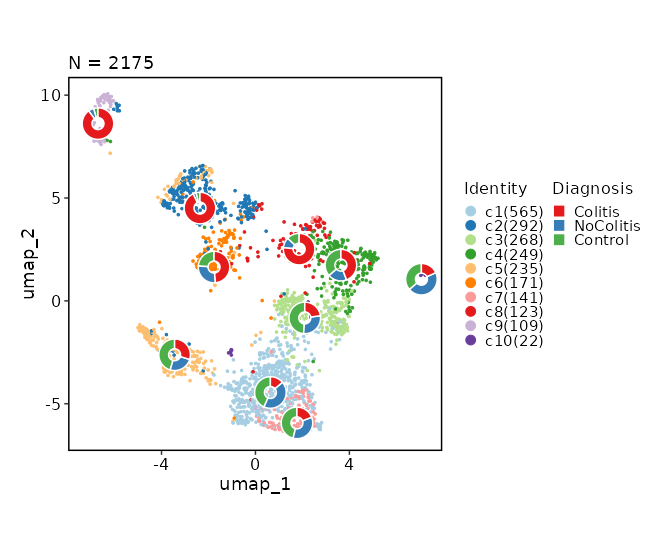 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
Dimensional reduction plot by Diagnosis
[SeuratClusterStats.envs.dimplots."Dimensional reduction plot by Diagnosis"]
facet_by = "Diagnosis"
highlight = true
theme = "theme_blank"
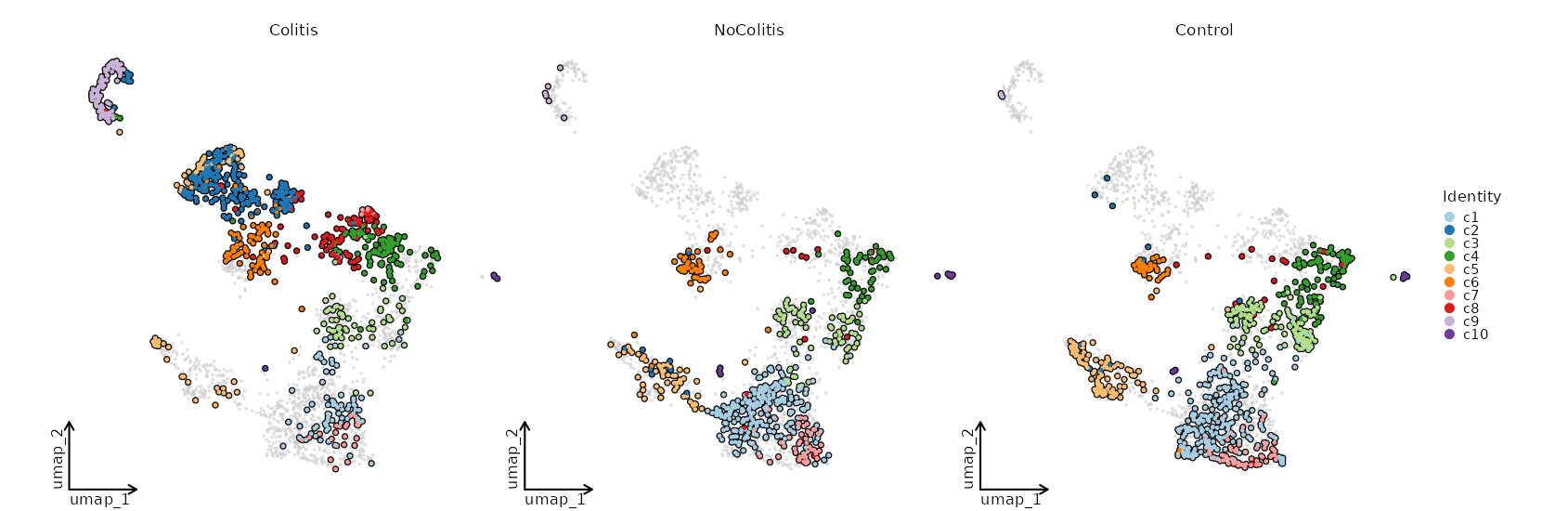 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
srtobj— The seurat object loaded bySeuratClustering
outdir— The output directory.Different types of plots will be saved in different subdirectories. For example,clustreeplots will be saved inclustreessubdirectory. For each case inenvs.clustrees, both the png and pdf files will be saved.
cache(type=auto) — Whether to cache the plots.Currently only plots for features are supported, since creating the those plots can be time consuming. IfTrue, the plots will be cached in the job output directory, which will be not cleaned up when job is rerunning.clustrees(type=json) — The cases for clustree plots.Keys are the names of the plots and values are the dicts inherited fromenv.clustrees_defaultsexceptprefix. There is no default case forclustrees.clustrees_defaults(ns) — The parameters for the clustree plots.- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the clustree plot.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - - more_formats (type=list): The formats to save the plots other than
png. - - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to reproduce the plot.
- - prefix (type=auto): string indicating columns containing clustering information.
The trailing dot is not necessary and will be added automatically.
WhenTRUE, clustrees will be plotted when there isFindClustersor
FindClusters.*in theobj@commands.
The latter is generated bySeuratSubClustering.
This will be ignored whenenvs.clustreesis specified
(the prefix of each case must be specified separately). - -
: Other arguments passed to scplotter::ClustreePlot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/ClustreePlot.html
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the clustree plot.
dimplots(type=json) — The dimensional reduction plots.Keys are the titles of the plots and values are the dicts inherited fromenv.dimplots_defaults. It can also have other parameters fromscplotter::CellDimPlot.dimplots_defaults(ns) — The default parameters fordimplots.- - group_by: The identity to use.
If it is from subclustering (reductionsub_umap_<ident>exists), this reduction will be used ifreduction
is set todimorauto. - - split_by: The column name in metadata to split the cells into different plots.
- - subset: An expression to subset the cells, will be passed to
tidyrseurat::filter(). - - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - - reduction (choice): Which dimensionality reduction to use.
- dim: UseSeurat::DimPlot.
First searches forumap, thentsne, thenpca.
Ifidentis from subclustering,sub_umap_<ident>will be used.
- auto: Same asdim
- umap: UseSeurat::UMAPPlot.
- tsne: UseSeurat::TSNEPlot.
- pca: UseSeurat::PCAPlot. - -
: See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/CellDimPlot.html
- - group_by: The identity to use.
features(type=json) — The plots for features, include gene expressions, and columns from metadata.Keys are the titles of the cases and values are the dicts inherited fromenv.features_defaults.features_defaults(ns) — The default parameters forfeatures.- - features (type=auto): The features to plot.
It can be either a string with comma separated features, a list of features, a file path withfile://prefix with features
(one per line), or an integer to use the top N features fromVariantFeatures(srtobj).
It can also be a dict with the keys as the feature group names and the values as the features, which
is used for heatmap to group the features. - - order_by (type=auto): The order of the clusters to show on the plot.
An expression passed todplyr::arrange()on the grouped meta data frame (byident).
For example, you can order the clusters by the activation score of
the cluster:desc(mean(ActivationScore, na.rm = TRUE)), suppose you have a column
ActivationScorein the metadata.
You may also specify the literal order of the clusters by a list of strings (at least two). - - subset: An expression to subset the cells, will be passed to
tidyrseurat::filter(). - - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - - descr: The description of the plot, showing in the report.
- - more_formats (type=list): The formats to save the plots other than
png. - - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to reproduce the plot.
- - save_data (flag): Whether to save the data used to generate the plot.
- -
: Other arguments passed to scplotter::FeatureStatPlot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/FeatureStatPlot.html
- - features (type=auto): The features to plot.
mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata to subset the cells.The mutaters will be applied in the order specified. You can also use the clone selectors to select the TCR clones/clusters. See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/clone_selectors.html.ngenes(type=json) — The number of genes expressed in each cell.Keys are the names of the plots and values are the dicts inherited fromenv.ngenes_defaults.ngenes_defaults(ns) — The default parameters forngenes.The default parameters to plot the number of genes expressed in each cell.- - more_formats (type=list): The formats to save the plots other than
png. - - subset: An expression to subset the cells, will be passed to
tidyrseurat::filter(). - - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots.
- - more_formats (type=list): The formats to save the plots other than
stats(type=json) — The number/fraction of cells to plot.Keys are the names of the plots and values are the dicts inherited fromenv.stats_defaults.stats_defaults(ns) — The default parameters forstats.This is to do some basic statistics on the clusters/cells. For more comprehensive analysis, see https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/CellStatPlot.html. The parameters from the cases can overwrite the default parameters.- - subset: An expression to subset the cells, will be passed to
tidyrseurat::filter(). - - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the clustree plot.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - - descr: The description of the plot, showing in the report.
- - more_formats (type=list): The formats to save the plots other than
png. - - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to reproduce the plot.
- - save_data (flag): Whether to save the data used to generate the plot.
- -
: Other arguments passed to scplotter::CellStatPlot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/CellStatPlot.html.
- - subset: An expression to subset the cells, will be passed to
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(Seurat)"
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.ModuleScoreCalculator(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Calculate the module scores for each cell
The module scores are calculated by
Seurat::AddModuleScore()
or Seurat::CellCycleScoring()
for cell cycle scores.
The module scores are calculated as the average expression levels of each program on single cell level, subtracted by the aggregated expression of control feature sets. All analyzed features are binned based on averaged expression, and the control features are randomly selected from each bin.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
srtobj— The seurat object loaded bySeuratClustering
rdsfile— The seurat object with module scores added to the metadata.
defaults(ns) — The default parameters formodules.- - features: The features to calculate the scores. Multiple features
should be separated by comma.
You can also specifycc.genesorcc.genes.updated.2019to
use the cell cycle genes to calculate cell cycle scores.
If so, three columns will be added to the metadata, including
S.Score,G2M.ScoreandPhase.
Only one type of cell cycle scores can be calculated at a time. - - nbin (type=int): Number of bins of aggregate expression levels
for all analyzed features. - - ctrl (type=int): Number of control features selected from
the same bin per analyzed feature. - - k (flag): Use feature clusters returned from
DoKMeans. - - assay: The assay to use.
- - seed (type=int): Set a random seed.
- - search (flag): Search for symbol synonyms for features in
features that don't match features in object? - - keep (flag): Keep the scores for each feature?
Only works for non-cell cycle scores. - - agg (choice): The aggregation function to use.
Only works for non-cell cycle scores.
- mean: The mean of the expression levels
- median: The median of the expression levels
- sum: The sum of the expression levels
- max: The max of the expression levels
- min: The min of the expression levels
- var: The variance of the expression levels
- sd: The standard deviation of the expression levels
- - features: The features to calculate the scores. Multiple features
modules(type=json) — The modules to calculate the scores.Keys are the names of the expression programs and values are the dicts inherited fromenv.defaults. Here are some examples -
For{ "CellCycle": {"features": "cc.genes.updated.2019"}, "Exhaustion": {"features": "HAVCR2,ENTPD1,LAYN,LAG3"}, "Activation": {"features": "IFNG"}, "Proliferation": {"features": "STMN1,TUBB"} }
CellCycle, the columnsS.Score,G2M.ScoreandPhasewill be added to the metadata.S.ScoreandG2M.Scoreare the cell cycle scores for each cell, andPhaseis the cell cycle phase for each cell.
You can also add Diffusion Components (DC) to the modules
{"DC": {"features": 2, "kind": "diffmap"}} will perform diffusion map as a reduction and add the first 2 components as
DC_1andDC_2to the metadata.diffmapis a shortcut fordiffusion_map. Other key-value pairs will pass todestiny::DiffusionMap(). You can later plot the diffusion map by usingreduction = "DC"inenv.dimplotsinSeuratClusterStats. This requiresSingleCellExperimentanddestinyR packages.
post_mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata aftercalculating the module scores. The mutaters will be applied in the order specified. This is useful when you want to create new scores based on the calculated module scores.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.CellsDistribution(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Distribution of cells (i.e. in a TCR clone) from different groupsfor each cluster
This generates a set of pie charts with proportion of cells in each cluster Rows are the cells identities (i.e. TCR clones or TCR clusters), columns are groups (i.e. clinic groups).
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
[CellsDistribution.envs.mutaters]# Add Patient1_Tumor_Expanded column with CDR3.aa that
# expands in Tumor of patient 1
Patient1_Tumor_Expanded = '''
expanded(., region, "Tumor", subset = patient == "Lung1", uniq = FALSE)
'''
[CellsDistribution.envs.cases.Patient1_Tumor_Expanded]
cells_by = "Patient1_Tumor_Expanded"
cells_orderby = "desc(CloneSize)"
group_by = "region"
group_order = [ "Tumor", "Normal" ]
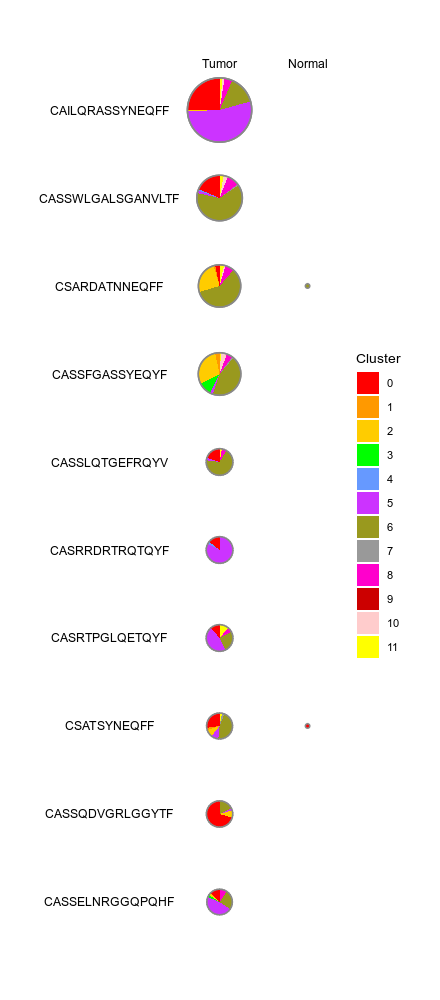
srtobj— The seurat object in RDS format
outdir— The output directory.The results for each case will be saved in a subdirectory.
cases(type=json;order=99) — If you have multiple cases, you can specify them here.Keys are the names of the cases and values are the options above exceptmutaters. If some options are not specified, the options inenvswill be used. If no cases are specified, a default case will be used with case nameDEFAULT.cells_by— The column name in metadata to group the cells for the rows of the plot.If your cell groups have overlapping cells, you can also use multiple columns, separated by comma (,). These columns will be concatenated to form the cell groups. For the overlapping cells, they will be counted multiple times for different groups. So make sure the cell group names in different columns are unique.cells_n(type=int) — The max number of groups to show for each cell group identity (row).Ignored ifcells_orderis specified.cells_order(list) — The order of the cells (rows) to show on the plotcells_orderby— An expression passed todplyr::arrange()to order the cells (rows) of the plot.Only works whencells-orderis not specified. The data frame passed todplyr::arrange()is grouped bycells_bybefore ordering. You can have multiple expressions separated by semicolon (;). The expessions will be parsed byrlang::parse_exprs(). 4 extra columns were added to the metadata for ordering the rows in the plot:- *
CloneSize: The size (number of cells) of clones (identified bycells_by) - *
CloneGroupSize: The clone size in each group (identified bygroup_by) - *
CloneClusterSize: The clone size in each cluster (identified byseurat_clusters) - *
CloneGroupClusterSize: The clone size in each group and cluster (identified bygroup_byandseurat_clusters)
- *
cluster_orderby— The order of the clusters to show on the plot.An expression passed todplyr::summarise()on the grouped data frame (byseurat_clusters). The summary stat will be passed todplyr::arrange()to order the clusters. It's applied on the whole meta.data before grouping and subsetting. For example, you can order the clusters by the activation score of the cluster:desc(mean(ActivationScore, na.rm = TRUE)), suppose you have a columnActivationScorein the metadata.descr— The description of the case, will be shown in the report.devpars(ns) — The device parameters for the plots of pie charts.- - res (type=int): The resolution of the plots
- - height (type=int): The height of the plots
- - width (type=int): The width of the plots
each— The column name in metadata to separate the cells into different plots.group_by— The column name in metadata to group the cells for the columns of the plot.group_order(list) — The order of the groups (columns) to show on the plothm_devpars(ns) — The device parameters for the heatmaps.- - res (type=int): The resolution of the heatmaps.
- - height (type=int): The height of the heatmaps.
- - width (type=int): The width of the heatmaps.
mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadataKeys are the names of the mutaters and values are the R expressions passed bydplyr::mutate()to mutate the metadata.overlap(list) — Plot the overlap of cell groups (values ofcells_by) in different casesunder the same section. The section must have at least 2 cases, each case should have a singlecells_bycolumn.prefix_each(flag) — Whether to prefix theeachcolumn name to thevalue as the case/section name.section— The section to show in the report. This allows different cases to be put in the same section in report.Only works wheneachis not specified.subset— An expression to subset the cells, will be passed todplyr::filter()on metadata.This will be applied prior toeach.
r-dplyr—- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(dplyr)"
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(Seurat)"
r-tidyr—- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(tidyr)"
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratMetadataMutater(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Mutate the metadata of the seurat object
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
metafile— Additional metadataA tab-delimited file with columns as meta columns and rows as cells.srtobj— The seurat object loaded by SeuratPreparing
outfile— The seurat object with the additional metadata
mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata.The key-value pairs will be passed thedplyr::mutate()to mutate the metadata.subset— An expression to subset the cells, will be passed todplyr::filter().This will be applied after mutating the metadata.
r-dplyr—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(dplyr)")
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(Seurat)")
r-tibble—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(tibble)")
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.DimPlots(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Seurat - Dimensional reduction plots
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
configfile— A toml configuration file with "cases"If this is given,envs.caseswill be overridenname— The name of the job, used in reportsrtobj— The seruat object in RDS format
outdir— The output directory
cases— The cases for the dim plotsKeys are the names and values are the arguments toSeurat::Dimplots
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.MarkersFinder(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Find markers between different groups of cells
When only group_by is specified as identity column in
envs.cases, the markers will be found for all the clusters.
You can also find the differentially expressed genes between
any two groups of cells by setting group_by to a different
column name in metadata. Follow envs.cases for more details.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
srtobj— The seurat object loaded bySeuratPreparingIf you have yourSeuratobject prepared by yourself, you can also use it here, but you should make sure that the object has been processed byPrepSCTFindMarkersif data is not normalized usingSCTransform.
outdir— The output directory for the markers and plots
allenrich_plots(type=json) — Cases of the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromallenrich_plots_defaults. The cases underenvs.casescan inherit this options.allenrich_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/EnrichmentPlot.html.
allmarker_plots(type=json) — All marker plot cases.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromallmarker_plots_defaults.allmarker_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots for all markers whenident_1is not specified.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/biopipen.utils.R/reference/VizDEGs.html.
Available types areviolin,box,bar,ridge,dim,heatmapanddot. - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: Other arguments passed to biopipen.utils::VizDEGs().
- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
assay— The assay to use.cache(type=auto) — Where to cache the results.IfTrue, cache tooutdirof the job. IfFalse, don't cache. Otherwise, specify the directory to cache to.cases(type=json) — If you have multiple cases for marker discovery, you can specify themhere. The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the above options. If some options are not specified, the default values specified above (underenvs) will be used. If no cases are specified, the default case will be added with the default values underenvswith the nameMarker Discovery.dbs(list) — The dbs to do enrichment analysis for significant markers.You can use built-in dbs inenrichit, or provide your own gmt files. See also https://pwwang.github.io/enrichit/reference/FetchGMT.html. The built-in dbs include:- * "BioCarta" or "BioCarta_2016"
- * "GO_Biological_Process" or "GO_Biological_Process_2025"
- * "GO_Cellular_Component" or "GO_Cellular_Component_2025"
- * "GO_Molecular_Function" or "GO_Molecular_Function_2025"
- * "KEGG", "KEGG_Human", "KEGG_2021", or "KEGG_2021_Human"
- * "Hallmark", "MSigDB_Hallmark", or "MSigDB_Hallmark_2020"
- * "Reactome", "Reactome_Pathways", or "Reactome_Pathways_2024"
- * "WikiPathways", "WikiPathways_2024", "WikiPathways_Human", or "WikiPathways_2024_Human"
each— The column name in metadata to separate the cells into differentcases. When this is specified, the case will be expanded for each value of the column in metadata. For example, when you haveenvs.cases."Cluster Markers".each = "Sample", then the case will be expanded asenvs.cases."Cluster Markers - Sample1",envs.cases."Cluster Markers - Sample2", etc. You can specifyallmarker_plotsandoverlapsto plot the markers for all cases in the same plot and plot the overlaps of the markers between different cases by values in this column.enrich_plots(type=json) — Cases of the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromenrich_plots_defaults. The cases underenvs.casescan inherit this options.enrich_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/EnrichmentPlot.html.
Available types arebar,dot,lollipop,network,enrichmapandwordcloud. - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/EnrichmentPlot.html.
- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
enrich_style(choice) — The style of the enrichment analysis.The enrichment analysis will be done byEnrichIt()fromenrichit. Two styles are available:- - enrichr:
enrichrstyle enrichment analysis (fisher's exact test will be used). - - clusterprofiler:
clusterProfilerstyle enrichment analysis (hypergeometric test will be used). - - clusterProfiler: alias for
clusterprofiler
- - enrichr:
error(flag) — Error out if no/not enough markers are found or no pathways are enriched.IfFalse, empty results will be returned.group_by— The column name in metadata to group the cells.If onlygroup_byis specified, andident_1andident_2are not specified, markers will be found for all groups in this column in the manner of "group vs rest" comparison.NAgroup will be ignored. IfNone,Seurat::Idents(srtobj)will be used, which is usually"seurat_clusters"after unsupervised clustering.ident_1— The first group of cells to compareWhen this is empty, the comparisons will be expanded to each group v.s. the rest of the cells ingroup_by.ident_2— The second group of cells to compareIf not provided, the rest of the cells are used forident_2.marker_plots(type=json) — Cases of the plots to generate for the markers.Plot cases. The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited frommarker_plots_defaults. The cases underenvs.casescan inherit this options.marker_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots to generate for the markers.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/biopipen.utils.R/reference/VizDEGs.html.
Available types areviolin,box,bar,ridge,dim,heatmapanddot.
There are two additional types available -volcano_pctandvolcano_log2fc. - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: Other arguments passed to biopipen.utils::VizDEGs().
Ifplot_typeisvolcano_pctorvolcano_log2fc, they will be passed to
scplotter::VolcanoPlot().
- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata.You can also use the clone selectors to select the TCR clones/clusters. See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/clone_selectors.html.ncores(type=int) — Number of cores to use for parallel computing for someSeuratprocedures.- * Used in
future::plan(strategy = "multicore", workers = <ncores>)to parallelize some Seurat procedures. - * See also: https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/future_vignette.html
- * Used in
overlaps(type=json) — Cases for investigating the overlapping of significant markers between different cases or comparisons.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromoverlaps_defaults. There are two situations that we can perform overlaps: 1. Ifident_1is not specified, the overlaps can be performed between different comparisons. 2. Ifeachis specified, the overlaps can be performed between different cases, where in each case,ident_1must be specified.overlaps_defaults(ns) — Default options for investigating the overlapping of significant markers between different cases or comparisons.This means eitherident_1should be empty, so that they can be expanded to multiple comparisons.- - sigmarkers: The expression to filter the significant markers for each case.
If not provided,envs.sigmarkerswill be used. - - plot_type (choice): The type of the plot to generate for the overlaps.
- venn: Useplotthis::VennDiagram().
- upset: Useplotthis::UpsetPlot(). - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: More arguments pased to plotthis::VennDiagram()
(https://pwwang.github.io/plotthis/reference/venndiagram1.html)
orplotthis::UpsetPlot()
(https://pwwang.github.io/plotthis/reference/upsetplot1.html)
- - sigmarkers: The expression to filter the significant markers for each case.
rest(ns) — Rest arguments forSeurat::FindMarkers().Use-to replace.in the argument name. For example, usemin-pctinstead ofmin.pct.sigmarkers— An expression passed todplyr::filter()to filter thesignificant markers for enrichment analysis. Available variables arep_val,avg_log2FC,pct.1,pct.2andp_val_adj. For example,"p_val_adj < 0.05 & abs(avg_log2FC) > 1"to select markers with adjusted p-value < 0.05 and absolute log2 fold change > 1.subset— An expression to subset the cells for each case.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.TopExpressingGenes(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Find the top expressing genes in each cluster
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
srtobj— The seurat object in RDS or qs/qs2 format
outdir— The output directory for the tables and plots
cases(type=json) — If you have multiple cases, you can specify themhere. The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the above options exceptmutaters. If some options are not specified, the default values specified above will be used. If no cases are specified, the default case will be added with the default values underenvswith the nameTop Expressing Genes.dbs(list) — The dbs to do enrichment analysis for significant markers.You can use built-in dbs inenrichit, or provide your own gmt files. See also https://pwwang.github.io/enrichit/reference/FetchGMT.html. The built-in dbs include:- * "BioCarta" or "BioCarta_2016"
- * "GO_Biological_Process" or "GO_Biological_Process_2025"
- * "GO_Cellular_Component" or "GO_Cellular_Component_2025"
- * "GO_Molecular_Function" or "GO_Molecular_Function_2025"
- * "KEGG", "KEGG_Human", "KEGG_2021", or "KEGG_2021_Human"
- * "Hallmark", "MSigDB_Hallmark", or "MSigDB_Hallmark_2020"
- * "Reactome", "Reactome_Pathways", or "Reactome_Pathways_2024"
- * "WikiPathways", "WikiPathways_2024", "WikiPathways_Human", or "WikiPathways_2024_Human"
each— The column name in metadata to separate the cells into differentcases.enrich_plots(type=json) — Cases of the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromenrich_plots_defaults. The cases underenvs.casescan inherit this options.enrich_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/EnrichmentPlot.html.
Available types arebar,dot,lollipop,network,enrichmapandwordcloud. - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/EnrichmentPlot.htmll.
- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
enrich_style(choice) — The style of the enrichment analysis.The enrichment analysis will be done byEnrichIt()fromenrichit. Two styles are available:- - enrichr:
enrichrstyle enrichment analysis (fisher's exact test will be used). - - clusterprofiler:
clusterProfilerstyle enrichment analysis (hypergeometric test will be used). - - clusterProfiler: alias for
clusterprofiler
- - enrichr:
group_by— The column name in metadata to group the cells.ident— The group of cells to find the top expressing genes.The cells will be selected by thegroup_bycolumn with thisidentvalue in metadata. If not provided, the top expressing genes will be found for all groups of cells in thegroup_bycolumn.mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata.You can also use the clone selectors to select the TCR clones/clusters. See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/clone_selectors.html.n(type=int) — The number of top expressing genes to find.subset— An expression to subset the cells for each case.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.ExprImputation(*args, **kwds) → Proc
This process imputes the dropout values in scRNA-seq data.
It takes the Seurat object as input and outputs the Seurat object with imputed expression data.
Reference:
- - Linderman, George C., Jun Zhao, and Yuval Kluger. "Zero-preserving imputation of scRNA-seq data using low-rank approximation." BioRxiv (2018): 397588.
- - Li, Wei Vivian, and Jingyi Jessica Li. "An accurate and robust imputation method scImpute for single-cell RNA-seq data." Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 997.
- - Dijk, David van, et al. "MAGIC: A diffusion-based imputation method reveals gene-gene interactions in single-cell RNA-sequencing data." BioRxiv (2017): 111591.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
infile— The input file in RDS/qs format of Seurat object
outfile— The output file in RDS format of Seurat objectNote that with rmagic and alra, the original default assay will be renamed toRAWand the imputed RNA assay will be renamed toRNAand set as default assay.
alra_args(type=json) — The arguments forRunALRA()rmagic_args(ns) — The arguments for rmagic- - python: The python path where magic-impute is installed.
- - threshold (type=float): The threshold for magic imputation.
Only the genes with dropout rates greater than this threshold (No. of
cells with non-zero expression / total number of cells) will be imputed.
scimpute_args(ns) — The arguments for scimpute- - drop_thre (type=float): The dropout threshold
- - kcluster (type=int): Number of clusters to use
- - ncores (type=int): Number of cores to use
- - refgene: The reference gene file
tool(choice) — Either alra, scimpute or rmagic- - alra: Use RunALRA() from Seurat
- - scimpute: Use scImpute() from scimpute
- - rmagic: Use magic() from Rmagic
magic-impute—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == "rmagic"}}
- check: {{proc.envs.rmagic_args.python}} -c "import magic")
r-dplyr—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == "scimpute"}}
- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(dplyr)")
r-rmagic—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == "rmagic"}}
- check: | {{proc.lang}} <( echo " tryCatch( { setwd(dirname(Sys.getenv('CONDA_PREFIX'))) }, error = function(e) NULL ); library(Rmagic) " )
r-scimpute—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == "scimpute"}}
- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(scImpute)")
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(Seurat)")
r-seuratwrappers—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == "alra"}}
- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library(SeuratWrappers)")
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SCImpute(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Impute the dropout values in scRNA-seq data.
Deprecated. Use ExprImputation instead.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
groupfile— The file to subset the matrix or label the cellsCould be an output from ImmunarchFilterinfile— The input file for imputationEither a SeuratObject or a matrix of count/TPM
outfile— The output matrix
infmt— The input format.Eitherseuratormatrix
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratFilter(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Filtering cells from a seurat object
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
filters— The filters to apply. Could be a file or string in TOML, ora python dictionary, with following keys:- - mutaters: Create new columns in the metadata
- - filter: A R expression that will pass to
subset(sobj, subset = ...)to filter the cells
srtobj— The seurat object in RDS
outfile— The filtered seurat object in RDS
invert— Invert the selection?
r-dplyr—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library('dplyr')")
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library('Seurat')")
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratSubset(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Subset a seurat object into multiple seruat objects
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
srtobj— The seurat object in RDSsubsets— The subsettings to apply. Could be a file or string in TOML, ora python dictionary, with following keys:- -
: Name of the case
mutaters: Create new columns in the metadata
subset: A R expression that will pass to
subset(sobj, subset = ...)
groupby: The column to group by, each value will be a case
If groupby is given, subset will be ignored, each value
of the groupby column will be a case
- -
outdir— The output directory with the subset seurat objects
ignore_nas— Ignore NA values?
r-dplyr—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library('dplyr')")
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} <(echo "library('Seurat')")
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratSplit(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Split a seurat object into multiple seruat objects
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
by— The metadata column to split bysrtobj— The seurat object in RDS
outdir— The output directory with the subset seurat objects
by— The metadata column to split byIgnored ifbyis given in the inputrecell— Rename the cell ids using thebycolumnA string of R function taking the original cell ids andby
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.Subset10X(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Subset 10X data, mostly used for testing
Requires r-matrix to load matrix.mtx.gz
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
indir— The input directory
outdir— The output directory
feats_to_keep— The features/genes to keep.The final features list will befeats_to_keep+nfeatsncells— The number of cells to keep.If <=1 then it will be the percentage of cells to keepnfeats— The number of features to keep.If <=1 then it will be the percentage of features to keepseed— The seed for random number generator
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratTo10X(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Write a Seurat object to 10X format
using write10xCounts from DropletUtils
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
srtobj— The seurat object in RDS
outdir— The output directory.Whenenvs.split_byis specified, the subdirectories will be created for each distinct value of the column. Otherwise, the matrices will be written to the output directory.
version— The version of 10X format
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.ScFGSEA(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Gene set enrichment analysis for cells in different groups using fgsea
This process allows us to do Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) on the expression data, but based on variaties of grouping, including the from the meta data and the scTCR-seq data as well.
The GSEA is done using the fgsea package, which allows to quickly and accurately calculate arbitrarily low GSEA P-values for a collection of gene sets. The fgsea package is based on the fast algorithm for preranked GSEA described in Subramanian et al. 2005.
For each case, the process will generate a table with the enrichment scores for each gene set, and GSEA plots for the top gene sets.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
The summary and GSEA plots
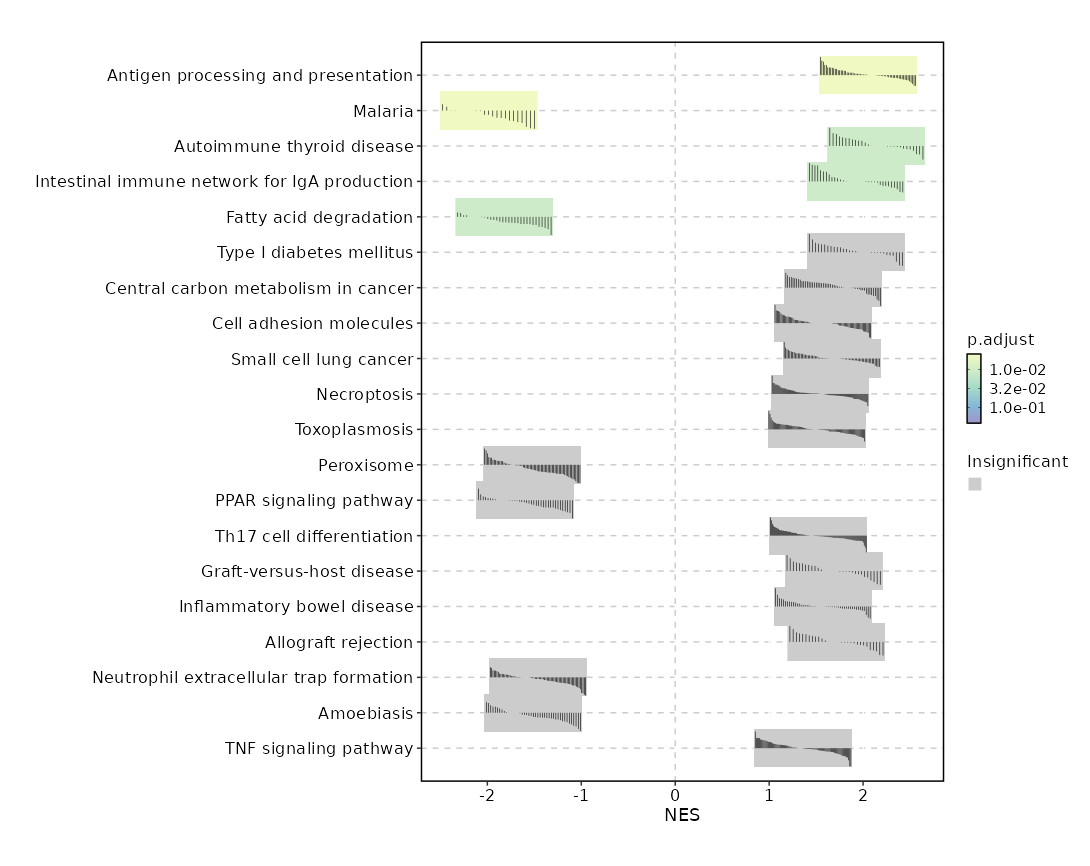 {: width="80%"}
{: width="80%"}
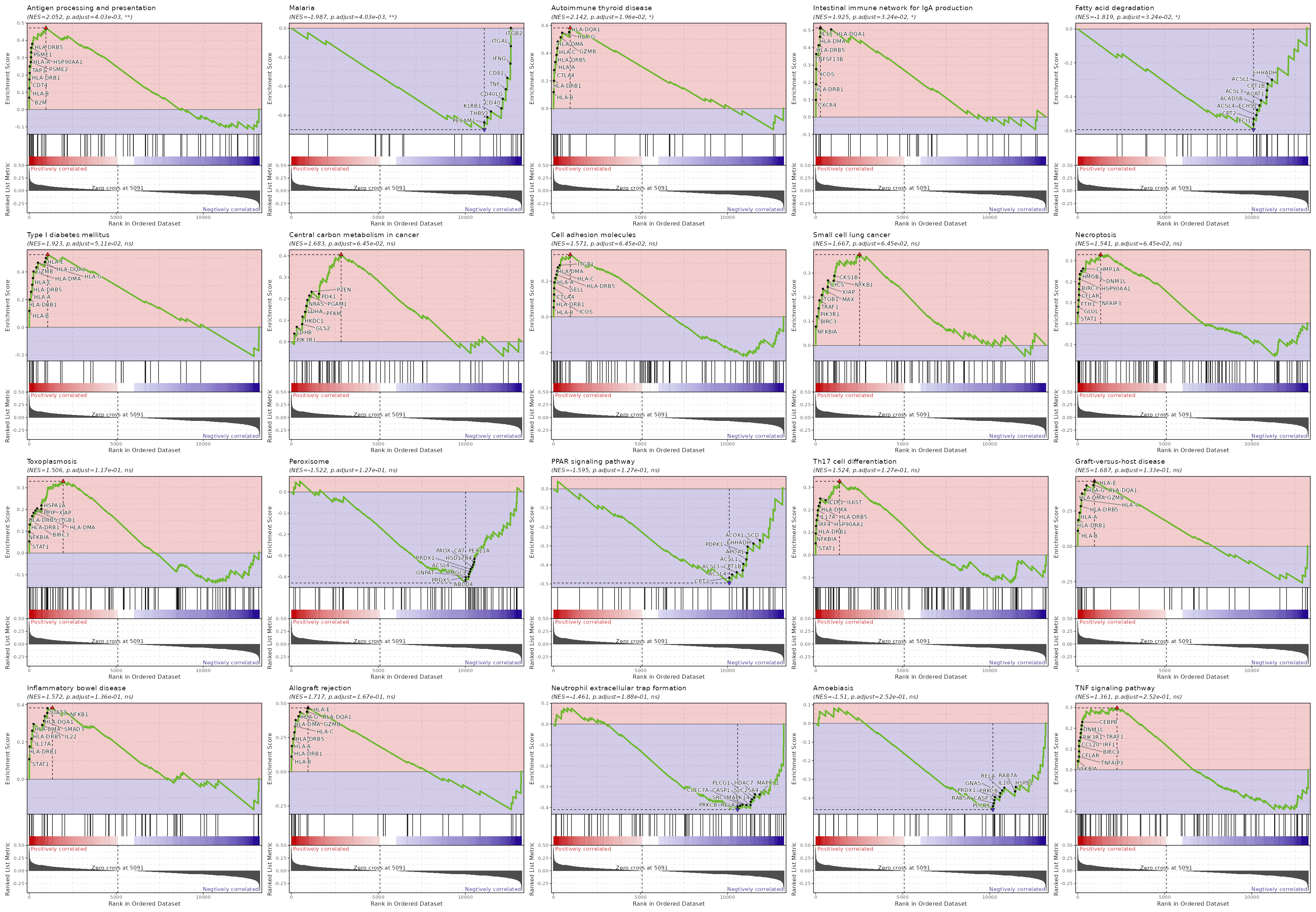 {: width="80%"}
{: width="80%"}
Summary plot for all subsets or idents
If you use each to separate the cells into different subsets, this is useful to
make a summary plot for all subsets. Or if you don't specify ident_1, the summary plot for all idents in group_by will be generated.
[ScFGSEA.envs]
group_by = "Diagnosis"
ident_1 = "Colitis"
ident_2 = "Control"
each = "seurat_clusters"
[ScFGSEA.envs.alleach_plots.Heatmap]
plot_type = "heatmap"
group_by = "Diagnosis"
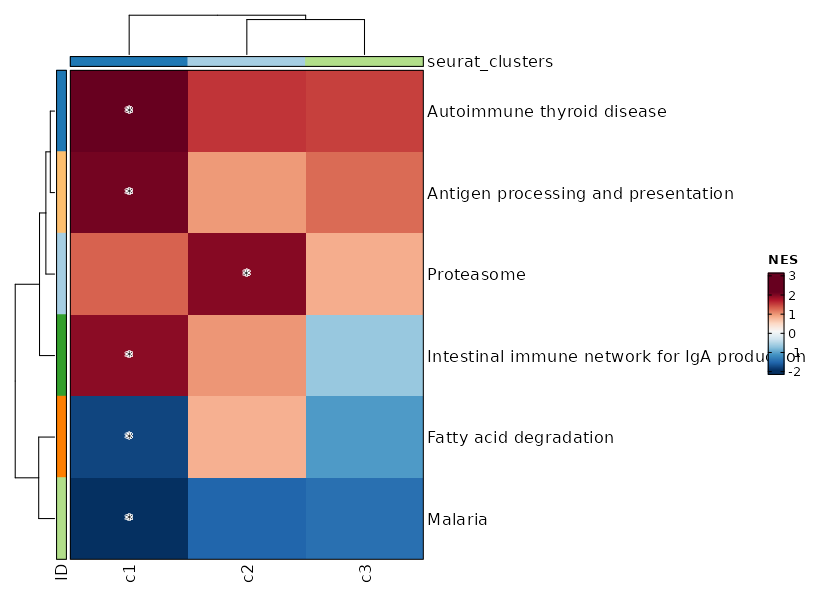 {: width="80%"}
{: width="80%"}
srtobj— The seurat object in RDS format
outdir— The output directory for the results and plots
alleach_plots(type=json) — Cases of the plots to generate for all pathways.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromalleach_plots_defaults.alleach_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots to generate for all pathways.- - plot_type: The type of the plot, currently either dot or heatmap (default)
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: See https://pwwang.github.io/biopipen.utils.R/reference/VizGSEA.html.
assay— The assay to use. If not provided, the default assay will be used.cache(type=auto) — Where to cache the results.IfTrue, cache tooutdirof the job. IfFalse, don't cache. Otherwise, specify the directory to cache to.cases(type=json;order=99) — If you have multiple cases, you can specify them here.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the above options exceptmutaters. If some options are not specified, the default values specified above will be used. If no cases are specified, the default case will be added with the nameGSEA.each— The column name in metadata to separate the cells into different subsets to do the analysis.eps(type=float) — This parameter sets the boundary for calculating the p value.See https://rdrr.io/bioc/fgsea/man/fgseaMultilevel.htmlgmtfile— The pathways in GMT format, with the gene names/ids in the same format as the seurat object.You can use built-in dbs inenrichit, or provide your own gmt files. See also https://pwwang.github.io/enrichit/reference/FetchGMT.html. The built-in dbs include:- * "BioCarta" or "BioCarta_2016"
- * "GO_Biological_Process" or "GO_Biological_Process_2025"
- * "GO_Cellular_Component" or "GO_Cellular_Component_2025"
- * "GO_Molecular_Function" or "GO_Molecular_Function_2025"
- * "KEGG", "KEGG_Human", "KEGG_2021", or "KEGG_2021_Human"
- * "Hallmark", "MSigDB_Hallmark", or "MSigDB_Hallmark_2020"
- * "Reactome", "Reactome_Pathways", or "Reactome_Pathways_2024"
- * "WikiPathways", "WikiPathways_2024", "WikiPathways_Human", or "WikiPathways_2024_Human"
group_by— The column name in metadata to group the cells.ident_1— The first group of cells to compareident_2— The second group of cells to compare, if not provided, the rest of the cells that are notNAs ingroup_bycolumn are used forident_2.maxsize(type=int) — Maximal size of a gene set to test. All pathways above the threshold are excluded.method(choice) — The method to do the preranking.- - signal_to_noise: Signal to noise.
The larger the differences of the means (scaled by the standard deviations);
that is, the more distinct the gene expression is in each phenotype and the more the gene
acts as a "class marker". - - s2n: Alias of signal_to_noise.
- - abs_signal_to_noise: The absolute value of signal_to_noise.
- - abs_s2n: Alias of abs_signal_to_noise.
- - t_test: T test.
Uses the difference of means scaled by the standard deviation and number of samples. - - ratio_of_classes: Also referred to as fold change.
Uses the ratio of class means to calculate fold change for natural scale data. - - diff_of_classes: Difference of class means.
Uses the difference of class means to calculate fold change for nature scale data - - log2_ratio_of_classes: Log2 ratio of class means.
Uses the log2 ratio of class means to calculate fold change for natural scale data.
This is the recommended statistic for calculating fold change for log scale data.
- - signal_to_noise: Signal to noise.
minsize(type=int) — Minimal size of a gene set to test. All pathways below the threshold are excluded.mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata.The key-value pairs will be passed thedplyr::mutate()to mutate the metadata. You can also use the clone selectors to select the TCR clones/clusters. See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/clone_selectors.html.ncores(type=int) — Number of cores for parallelizationPassed tonprocoffgseaMultilevel().rest(type=json;order=98) — Rest arguments forfgsea()See also https://rdrr.io/bioc/fgsea/man/fgseaMultilevel.htmlsubset— An expression to subset the cells.top(type=auto) — Do gsea table and enrich plot for top N pathways.If it is < 1, will apply it topadj, selecting pathways withpadj<top.
bioconductor-fgsea—- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(fgsea)"
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(seurat)"
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.CellTypeAnnotation(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Annotate the cell clusters. Currently, four ways are supported:
- Pass the cell type annotation directly
- Use
ScType - Use
scCATCH - Use
hitype - Use
celltypist
The annotated cell types will replace the original identity column in the metadata, so that the downstream processes will use the annotated cell types.
/// Note
When cell types are annotated, the original identity column (e.g. seurat_clusters) will be renamed
to envs.backup_col (e.g. seurat_clusters_id), and the new identity column will be added.
///
If you are using ScType, scCATCH, or hitype, a text file containing the mapping from
the original identity to the new cell types will be generated and saved to
cluster2celltype.tsv under <workdir>/<pipline_name>/CellTypeAnnotation/0/output/.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
[CellTypeAnnotation.envs]tool = "direct"
cell_types = ["CellType1", "CellType2", "-", "CellType4"]
The cell types will be assigned as:
0 -> CellType1
1 -> CellType2
2 -> 2
3 -> CellType4
sobjfile— The single-cell object in RDS/qs/qs2/h5ad format.
outfile— The rds/qs/qs2/h5ad file of seurat object with cell type annotated.A text file containing the mapping from the old identity to the new cell types will be generated and saved tocluster2celltype.tsvunder the job output directory. Note that ifenvs.identis specified, the output Seurat object will have the identity set to the specified column in metadata.
backup_col— The backup column name to store the original identities.If not specified, the original identity column will not be stored. Ifenvs.newcolis specified, this will be ignored.cell_types(type=auto) — The cell types to use for direct annotation.If given as a list (array), you can use"-"or""as the placeholder for the clusters that you want to keep the original cell types. If the length ofcell_typesis shorter than the number of clusters, the remaining clusters will be kept as the original cell types. You can also useNAto remove the clusters from downstream analysis. This only works whenenvs.newcolis not specified. If given as a dict (map), the keys are the original cluster names and the values are the new cell types.
/// Note Iftoolisdirectandcell_typesis not specified or an empty list, the original cell types will be kept and nothing will be changed. ///celltypist_args(ns) — The arguments forcelltypist::celltypist()iftooliscelltypist.- - model: The path to model file.
- - python: The python path where celltypist is installed.
- - majority_voting: When true, it refines cell identities within local subclusters after an over-clustering approach
at the cost of increased runtime. - - over_clustering (type=auto): The column name in metadata to use as clusters for majority voting.
Set toFalseto disable over-clustering.
Whenin.sobjfileis rds/qs/qs2 (supposing we have a Seurat object), the default ident is used by default.
Otherwise, it is False by default. - - assay: When converting a Seurat object to AnnData, the assay to use.
If input is h5seurat, this defaults to RNA.
If input is Seurat object in RDS, this defaults to the default assay.
hitype_db— The database to use for hitype.Compatible withsctype_db. See also https://pwwang.github.io/hitype/articles/prepare-gene-sets.html You can also use built-in databases, includinghitypedb_short,hitypedb_full, andhitypedb_pbmc3k.hitype_tissue— The tissue to use forhitype.Avaiable tissues should be the first column (tissueType) ofhitype_db. If not specified, all rows inhitype_dbwill be used.ident— The column name in metadata to use as the clusters.If not specified, the identity column will be used when input is rds/qs/qs2 (supposing we have a Seurat object). If input data is h5ad, this is required to run cluster-based annotation tools. Forcelltypist, this is a shortcut to setover_clusteringincelltypist_args.merge(flag) — Whether to merge the clusters with the same cell types.Otherwise, a suffix will be added to the cell types (ie..1,.2, etc).more_cell_types(type=json) — The additional cell type annotations to add to the metadata.The keys are the new column names and the values are the cell types lists. The cell type lists work the same ascell_typesabove. This is useful when you want to keep multiple annotations of cell types.newcol— The new column name to store the cell types.If not specified, the identity column will be overwritten. If specified, the original identity column will be kept andIdentswill be kept as the original identity.outtype(choice) — The output file type. Currently only works forcelltypist.An RDS file will be generated for other tools.- - input: Use the same file type as the input.
- - rds: Use RDS file.
- - qs: Use qs2 file.
- - qs2: Use qs2 file.
- - h5ad: Use AnnData file.
sccatch_args(ns) — The arguments forscCATCH::findmarkergene()iftoolissccatch.- - species: The specie of cells.
- - cancer: If the sample is from cancer tissue, then the cancer type may be defined.
- - tissue: Tissue origin of cells must be defined.
- - marker: The marker genes for cell type identification.
- - if_use_custom_marker (flag): Whether to use custom marker genes. If
True, nospecies,cancer, andtissueare needed. - -
: Other arguments for scCATCH::findmarkergene().
You can pass an RDS file tosccatch_args.markerto work as custom marker. If so,
if_use_custom_markerwill be set toTRUEautomatically.
sctype_db— The database to use for sctype.Check examples at https://github.com/IanevskiAleksandr/sc-type/blob/master/ScTypeDB_full.xlsxsctype_tissue— The tissue to use forsctype.Avaiable tissues should be the first column (tissueType) ofsctype_db. If not specified, all rows insctype_dbwill be used.tool(choice) — The tool to use for cell type annotation.- - sctype: Use
scTypeto annotate cell types.
See https://github.com/IanevskiAleksandr/sc-type - - hitype: Use
hitypeto annotate cell types.
See https://github.com/pwwang/hitype - - sccatch: Use
scCATCHto annotate cell types.
See https://github.com/ZJUFanLab/scCATCH - - celltypist: Use
celltypistto annotate cell types.
See https://github.com/Teichlab/celltypist - - direct: Directly assign cell types
- - sctype: Use
r-HGNChelper—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == 'sctype'}}
- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(HGNChelper)"
r-dplyr—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == 'sctype'}}
- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(dplyr)"
r-openxlsx—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == 'sctype'}}
- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(openxlsx)"
r-seurat—- if: {{proc.envs.tool == 'sctype'}}
- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(Seurat)"
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.SeuratMap2Ref(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Map the seurat object to reference
See: https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/integration_mapping.html and https://satijalab.org/seurat/articles/multimodal_reference_mapping.html
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
sobjfile— The seurat object
outfile— The rds file of seurat object with cell type annotated.Note that the reduction name will beref.umapfor the mapping. To visualize the mapping, you should useref.umapas the reduction name.
FindTransferAnchors(ns) — Arguments forFindTransferAnchors()- - normalization-method (choice): Name of normalization method used.
- LogNormalize: Log-normalize the data matrix
- SCT: Scale data using the SCTransform method
- auto: Automatically detect the normalization method.
Seeenvs.refnorm. - - reference-reduction: Name of dimensional reduction to use from the reference if running the pcaproject workflow.
Optionally enables reuse of precomputed reference dimensional reduction. - -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/findtransferanchors.
Note that the hyphen (-) will be transformed into.for the keys.
- - normalization-method (choice): Name of normalization method used.
MapQuery(ns) — Arguments forMapQuery()- - reference-reduction: Name of reduction to use from the reference for neighbor finding
- - reduction-model:
DimReducobject that contains the umap model. - - refdata (type=json): Extra data to transfer from the reference to the query.
- -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/mapquery.
Note that the hyphen (-) will be transformed into.for the keys.
NormalizeData(ns) — Arguments forNormalizeData()- - normalization-method: Normalization method.
- -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/normalizedata.
Note that the hyphen (-) will be transformed into.for the keys.
SCTransform(ns) — Arguments forSCTransform()- - do-correct-umi (flag): Place corrected UMI matrix in assay counts layer?
- - do-scale (flag): Whether to scale residuals to have unit variance?
- - do-center (flag): Whether to center residuals to have mean zero?
- -
: See https://satijalab.org/seurat/reference/sctransform.
Note that the hyphen (-) will be transformed into.for the keys.
cache(type=auto) — Whether to cache the information at different steps.IfTrue, the seurat object will be cached in the job output directory, which will be not cleaned up when job is rerunning. The cached seurat object will be saved as<signature>.<kind>.RDSfile, where<signature>is the signature determined by the input and envs of the process. See https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/issues/7849, https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/issues/5358 and https://github.com/satijalab/seurat/issues/6748 for more details also about reproducibility issues. To not use the cached seurat object, you can either setcachetoFalseor delete the cached file at<signature>.RDSin the cache directory.ident— The name of the ident for query transferred fromenvs.useof the reference.mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadata.This is helpful when we want to create new columns forsplit_by.ncores(type=int;order=-100) — Number of cores to use.Whensplit_byis used, this will be the number of cores for each object to map to the reference. Whensplit_byis not used, this is used infuture::plan(strategy = "multicore", workers = <ncores>)to parallelize some Seurat procedures. See also: https://satijalab.org/seurat/archive/v3.0/future_vignette.htmlplots(type=json) — The plots to generate.The keys are the names of the plots and the values are the arguments for the plot. The arguments will be passed tobiopipen.utils::VizSeuratMap2Ref()to generate the plots. The plots will be saved to the output directory. See https://pwwang.github.io/biopipen.utils.R/reference/VizSeuratMap2Ref.html.ref— The reference seurat object file.Either an RDS file or a h5seurat file that can be loaded bySeurat::LoadH5Seurat(). The file type is determined by the extension..rdsor.RDSfor RDS file,.h5seurator.h5for h5seurat file.refnorm(choice) — Normalization method the reference used. The same method will be used for the query.- - LogNormalize: Using
NormalizeData. - - SCTransform: Using
SCTransform. - - SCT: Alias of SCTransform.
- - auto: Automatically detect the normalization method.
If the default assay of reference isSCT, thenSCTransformwill be used.
- - LogNormalize: Using
skip_if_normalized— Skip normalization if the query is already normalized.Since the object is supposed to be generated bySeuratPreparing, it is already normalized. However, a different normalization method may be used. If the reference is normalized by the same method as the query, the normalization can be skipped. Otherwise, the normalization cannot be skipped. The normalization method used for the query set is determined by the default assay. IfSCT, thenSCTransformis used; otherwise,NormalizeDatais used. You can set this toFalseto force re-normalization (with or without the arguments previously used).split_by— The column name in metadata to split the query into multiple objects.This helps when the original query is too large to process.use— A column name of metadata from the reference(e.g.celltype.l1,celltype.l2) to transfer to the query as the cell types (ident) for downstream analysis. This field is required. If you want to transfer multiple columns, you can useenvs.MapQuery.refdata.
r-seurat—- check: {{proc.lang}} -e "library(Seurat)"
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.RadarPlots(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Radar plots for cell proportion in different clusters.
This process generates the radar plots for the clusters of T cells. It explores the proportion of cells in different groups (e.g. Tumor vs Blood) in different T-cell clusters.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
Let's say we have a metadata like this:
| Cell | Source | Timepoint | seurat_clusters |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Blood | Pre | 0 |
| B | Blood | Pre | 0 |
| C | Blood | Post | 1 |
| D | Blood | Post | 1 |
| E | Tumor | Pre | 2 |
| F | Tumor | Pre | 2 |
| G | Tumor | Post | 3 |
| H | Tumor | Post | 3 |
With configurations:
[RadarPlots.envs]
by = "Source"
Then we will have a radar plots like this:
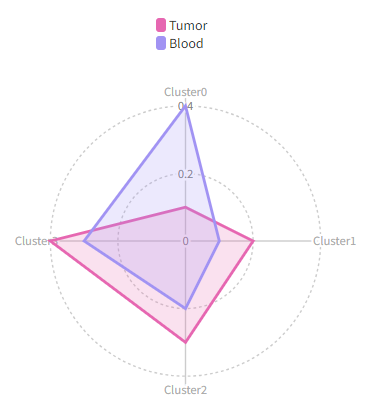
We can use each to separate the cells into different cases:
[RadarPlots.envs]
by = "Source"
each = "Timepoint"
Then we will have two radar plots, one for Pre and one for Post:
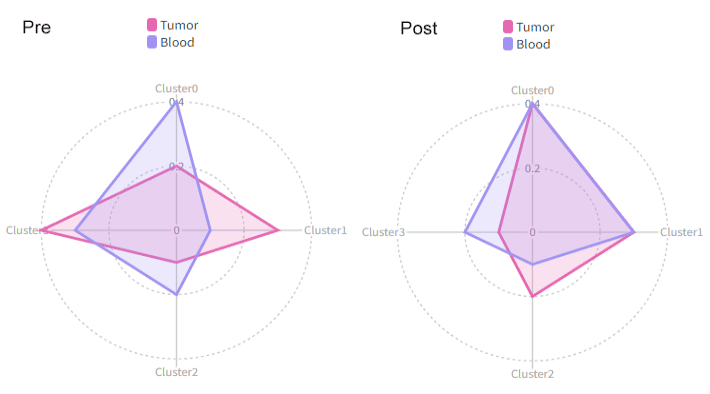
Using cluster_order to change the order of the clusters and show only the first 3 clusters:
[RadarPlots.envs]
by = "Source"
cluster_order = ["2", "0", "1"]
breaks = [0, 50, 100] # also change the breaks
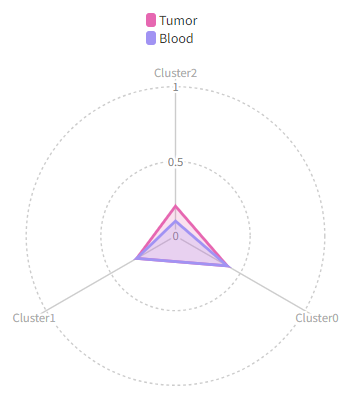
n. /
srtobj— The seurat object in RDS or qs/qs2 format
outdir— The output directory for the plots
bar_devpars(ns) — The parameters forpng()for the barplot- - res (type=int): The resolution of the plot
- - height (type=int): The height of the plot
- - width (type=int): The width of the plot
breakdown— An additional column with groups to break down the cellsdistribution in each cluster. For example, if you want to see the distribution of the cells in each cluster in different samples. In this case, you should have multiple values in eachby. These values won't be plotted in the radar plot, but a barplot will be generated with the mean value of each group and the error bar.breaks(list;itype=int) — breaks of the radar plots, from 0 to 100.If not given, the breaks will be calculated automatically.by— Which column to use to separate the cells in different groups.NAs will be ignored. For example, If you have a column namedSourcethat marks the source of the cells, and you want to separate the cells intoTumorandBloodgroups, you can setbytoSource. The there will be two curves in the radar plot, one forTumorand one forBlood.cases(type=json) — The cases for the multiple radar plots.Keys are the names of the cases and values are the arguments for the plots (each,by,order,breaks,direction,ident,cluster_orderanddevpars). If not cases are given, a default case will be used, with the keyDEFAULT. The keys must be valid string as part of the file name.cluster_order(list) — The order of the clusters.You may also use it to filter the clusters. If not given, all clusters will be used. If the cluster names are integers, use them directly for the order, even though a prefixClusteris added on the plot.colors— The colors for the groups inby. If not specified,the default colors will be used. Multiple colors can be separated by comma (,). You can specifybiopipento use thebiopipenpalette.devpars(ns) — The parameters forpng()- - res (type=int): The resolution of the plot
- - height (type=int): The height of the plot
- - width (type=int): The width of the plot
direction(choice) — Direction to calculate the percentages.- - inter-cluster: the percentage of the cells in all groups
in each cluster (percentage adds up to 1 for each cluster). - - intra-cluster: the percentage of the cells in all clusters.
(percentage adds up to 1 for each group).
- - inter-cluster: the percentage of the cells in all groups
each— A column with values to separate all cells in different casesWhen specified, the case will be expanded to multiple cases for each value in the column. If specified,sectionwill be ignored, and the case name will be used as the section name.ident— The column name of the cluster information.mutaters(type=json) — Mutaters to mutate the metadata of theseurat object. Keys are the column names and values are the expressions to mutate the columns. These new columns will be used to define your cases.order(list) — The order of the values inby. You can also limit(filter) the values we have inby. For example, if columnSourcehas valuesTumor,Blood,Spleen, and you only want to plotTumorandBlood, you can setorderto["Tumor", "Blood"]. This will also haveTumoras the first item in the legend andBloodas the second item.prefix_each(flag) — Whether to prefix theeachcolumn name to the values as thecase/section name.section— If you want to put multiple cases into a same sectionin the report, you can set this option to the name of the section. Only used in the report.subset— The subset of the cells to do the analysis.test(choice) — The test to use to calculate the p values.If there are more than 2 groups inby, the p values will be calculated pairwise group by group. Only works whenbreakdownis specified andbyhas 2 groups or more.- - wilcox: Wilcoxon rank sum test
- - t: T test
- - none: No test will be performed
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.MetaMarkers(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Find markers between three or more groups of cells, using one-way ANOVAor Kruskal-Wallis test.
Sometimes, you may want to find the markers for cells from more than 2 groups. In this case, you can use this process to find the markers for the groups and do enrichment analysis for the markers. Each marker is examined using either one-way ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis test. The p values are adjusted using the specified method. The significant markers are then used for enrichment analysis using enrichr api.
Other than the markers and the enrichment analysis as outputs, this process also generates violin plots for the top 10 markers.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
srtobj— The seurat object loaded bySeuratPreparing
outdir— The output directory for the markers
cases(type=json) — If you have multiple cases, you can specify themhere. The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the above options exceptncoresandmutaters. If some options are not specified, the default values specified above will be used. If no cases are specified, the default case will be added with the default values underenvswith the nameDEFAULT.dbs(list) — The dbs to do enrichment analysis for significant markers.You can use built-in dbs inenrichit, or provide your own gmt files. See also https://pwwang.github.io/enrichit/reference/FetchGMT.html. The built-in dbs include:- * "BioCarta" or "BioCarta_2016"
- * "GO_Biological_Process" or "GO_Biological_Process_2025"
- * "GO_Cellular_Component" or "GO_Cellular_Component_2025"
- * "GO_Molecular_Function" or "GO_Molecular_Function_2025"
- * "KEGG", "KEGG_Human", "KEGG_2021", or "KEGG_2021_Human"
- * "Hallmark", "MSigDB_Hallmark", or "MSigDB_Hallmark_2020"
- * "Reactome", "Reactome_Pathways", or "Reactome_Pathways_2024"
- * "WikiPathways", "WikiPathways_2024", "WikiPathways_Human", or "WikiPathways_2024_Human"
each— The column name in metadata to separate the cells into different cases.group-by— The column name in metadata to group the cells.If onlygroup-byis specified, andidentsare not specified, markers will be found for all groups in this column.NAgroup will be ignored.idents— The groups of cells to compare, values should be in thegroup-bycolumn.method(choice) — The method for the test.- - anova: One-way ANOVA
- - kruskal: Kruskal-Wallis test
mutaters(type=json) — The mutaters to mutate the metadataThe key-value pairs will be passed thedplyr::mutate()to mutate the metadata.ncores(type=int) — Number of cores to use to parallelize for genesp_adjust(choice) — The method to adjust the p values, which can be used to filter the significant markers.See also https://rdrr.io/r/stats/p.adjust.html- - holm: Holm-Bonferroni method
- - hochberg: Hochberg method
- - hommel: Hommel method
- - bonferroni: Bonferroni method
- - BH: Benjamini-Hochberg method
- - BY: Benjamini-Yekutieli method
- - fdr: FDR method of Benjamini-Hochberg
- - none: No adjustment
prefix_each(flag) — Whether to add theeachvalue as prefix to the case name.section— The section name for the report.Worked only wheneachis not specified. Otherwise, the section name will be constructed fromeachandgroup-by. IfDEFAULT, and it's the only section, it not included in the case/section names.sigmarkers— An expression passed todplyr::filter()to filter thesignificant markers for enrichment analysis. The default isp.value < 0.05. Ifmethod = 'anova', the variables that can be used for filtering are:sumsq,meansq,statistic,p.valueandp_adjust. Ifmethod = 'kruskal', the variables that can be used for filtering are:statistic,p.valueandp_adjust.subset— The subset of the cells to do the analysis.An expression passed todplyr::filter().
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.Seurat2AnnData(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Convert seurat object to AnnData
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
sobjfile— The seurat object file, in RDS or qs/qs2 format
outfile— The AnnData file
assay— The assay to use for AnnData.If not specified, the default assay will be used.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.AnnData2Seurat(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Convert AnnData to seurat object
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
adfile— The AnnData .h5ad file
outfile— The seurat object file in RDS or qs/qs2 format
assay— The assay to use to convert to seurat object.dotplot_check(type=auto) — Whether to do a check with a dot plot.(scplotter::FeatureStatPlot(plot_type = "dot", ..)will be used) to see if the conversion is successful. Set toFalseto disable the check. IfTrue, top 10 variable genes will be used for the check. You can give a list of genes or a string of genes with comma (,) separated to use for the check.ident— The column name inadfile.obsto use as the identityfor the seurat object. If not specified, no identity will be set.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.ScSimulation(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Simulate single-cell data using splatter.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
seed— The seed for the simulationYou could also use string as the seed, and the seed will be generated bydigest::digest2int(). So this could also work as a unique identifier for the simulation (ie. Sample ID).
outfile— The output Seurat object/SingleCellExperiment in qs/qs2 format
method(choice) — which simulation method to use. Options are:- - single: produces a single population
- - groups: produces distinct groups (eg. cell types), or
- - paths: selects cells from continuous trajectories (eg. differentiation processes)
ncells(type=int) — The number of cells to simulatengenes(type=int) — The number of genes to simulatenspikes(type=int) — The number of spike-ins to simulateWhenngenes,ncells, andnspikesare not specified, the default params frommockSCE()will be used. By default,ngenes = 2000,ncells = 200, andnspikes = 100.outtype(choice) — The output file type.- - seurat: Seurat object
- - singlecellexperiment: SingleCellExperiment object
- - sce: alias for
singlecellexperiment
params(ns) — Other parameters for simulation.The parameters are initializedsplitEstimate(mockSCE())and then updated with the given parameters. See https://rdrr.io/bioc/splatter/man/SplatParams.html. Hyphens (-) will be transformed into dots (.) for the keys.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.CellCellCommunication(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Cell-cell communication inference
This is implemented based on LIANA, which is a Python package for cell-cell communication inference and provides a list of existing methods including CellPhoneDB, Connectome, log2FC, NATMI, SingleCellSignalR, Rank_Aggregate, Geometric Mean, scSeqComm, and CellChat.
You can also try python -c 'import liana; liana.mt.show_methods()' to see the methods available.
Note that this process does not do any visualization. You can use CellCellCommunicationPlots
to visualize the results.
Reference:
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
sobjfile— The seurat object file in RDS or h5seurat format or AnnData file.
outfile— The output file with the 'liana_res' data frame.Stats are provided for both ligand and receptor entities, more specifically: ligand and receptor are the two entities that potentially interact. As a reminder, CCC events are not limited to secreted signalling, but we refer to them as ligand and receptor for simplicity. Also, in the case of heteromeric complexes, the ligand and receptor columns represent the subunit with minimum expression, while *complex corresponds to the actual complex, with subunits being separated by . source and target columns represent the source/sender and target/receiver cell identity for each interaction, respectively- *
*_props: represents the proportion of cells that express the entity.
By default, any interactions in which either entity is not expressed in above 10%% of cells per cell type
is considered as a false positive, under the assumption that since CCC occurs between cell types, a sufficient
proportion of cells within should express the genes. - *
*_means: entity expression mean per cell type. - *
lr_means: mean ligand-receptor expression, as a measure of ligand-receptor interaction magnitude. - *
cellphone_pvals: permutation-based p-values, as a measure of interaction specificity.
ligand ligand_complex ligand_props ligand_trimean mat_max receptor receptor_complex receptor_props receptor_trimean source target lr_probs cellchat_pvals mag_score spec_score VIM VIM 1.00 0.36 8.73 CD44 CD44 0.77 0.16 c7 c3 0.10 0.00 0.10 0.00 MIF MIF 0.97 0.22 8.73 CXCR4 CD74_CXCR4 0.87 0.26 c5 c6 0.10 0.00 0.10 0.00 HLA-B HLA-B 1.00 0.44 8.73 KLRD1 KLRD1 0.73 0.13 c9 c2 0.10 0.00 0.10 0.00 HMGB1 HMGB1 0.99 0.26 8.73 CXCR4 CXCR4 0.81 0.21 c2 c7 0.10 0.00 0.10 0.00 CD48 CD48 0.94 0.20 8.73 CD2 CD2 0.99 0.28 c7 c8 0.10 0.00 0.10 0.00 HLA-C HLA-C 1.00 0.38 8.73 CD8B CD8B 0.73 0.15 c1 c9 0.10 0.00 0.10 0.00 LGALS1 LGALS1 0.95 0.17 8.73 CD69 CD69 0.99 0.34 c10 c5 0.10 0.00 0.10 0.00 - *
help(liana.mt.<method>.__call__)in Python.assay— The assay to use for the analysis.Only works for Seurat object.expr_prop(type=float) — Minimum expression proportion for the ligands andreceptors (+ their subunits) in the corresponding cell identities. Set to 0 to return unfiltered results.group_by— alias forgroupbygroupby— The column name in metadata to group the cells.Typically, this column should be the cluster id. If provided input is a Seurat object, the default identity will be used by default. Otherwise, it is recommended to provide this parameter. "seurat_clusters" will be used with a warning if the input is in AnnData format and this parameter is not provided.method(choice) — The method to use for cell-cell communication inference.- - CellPhoneDB: Use CellPhoneDB method.
Magnitude Score: lr_means; Specificity Score: cellphone_pvals. - - Connectome: Use Connectome method.
- - log2FC: Use log2FC method.
- - NATMI: Use NATMI method.
- - SingleCellSignalR: Use SingleCellSignalR method.
- - Rank_Aggregate: Use Rank_Aggregate method.
- - Geometric_Mean: Use Geometric Mean method.
- - scSeqComm: Use scSeqComm method.
- - CellChat: Use CellChat method.
- - cellphonedb: alias for
CellPhoneDB - - connectome: alias for
Connectome - - log2fc: alias for
log2FC - - natmi: alias for
NATMI - - singlesignaler: alias for
SingleCellSignalR - - rank_aggregate: alias for
Rank_Aggregate - - geometric_mean: alias for
Geometric_Mean - - scseqcomm: alias for
scSeqComm - - cellchat: alias for
CellChat
- - CellPhoneDB: Use CellPhoneDB method.
min_cells(type=int) — Minimum cells (per cell identity if grouped bygroupby)to be considered for downstream analysis.n_perms(type=int) — Number of permutations for the permutation test.Relevant only for permutation-based methods (e.g.,CellPhoneDB). If0is passed, no permutation testing is performed.ncores(type=int) — The number of cores to use.rscript— The path to the Rscript executable used to convert RDS file to AnnData.ifin.sobjfileis an RDS file, it will be converted to AnnData file (h5ad). You needSeurat,SeuratDiskanddigestinstalled.seed(type=int) — The seed for the random number generator.species(choice) — The species of the cells.- - human: Human cells, the 'consensus' resource will be used.
- - mouse: Mouse cells, the 'mouseconsensus' resource will be used.
split_by— The column name in metadata to split the cells to run the method separately.The results will be combined together with this column in the final output.subset— An expression in string to subset the cells.When a.rdsor.h5seuratfile is provided forin.sobjfile, you can provide an expression inR, which will be passed tobase::subset()inRto subset the cells. But you can always pass an expression inpythonto subset the cells. See https://anndata.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/notebooks/getting-started.html#subsetting-using-metadata. You should useadatato refer to the AnnData object. For example,adata.obs.groups == "g1"will subset the cells withgroupsequal tog1.subset_using— The method to subset the cells.- - auto: Automatically detect the method to use.
Note that this is not always accurate. We simply check if[is in the expression.
If so, we usepythonto subset the cells; otherwise, we useR. - - python: Use python to subset the cells.
- - r: Use R to subset the cells.
- - auto: Automatically detect the method to use.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.CellCellCommunicationPlots(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Visualization for cell-cell communication inference.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
Network Plot
[CellCellCommunicationPlots.envs.cases."Cell-Cell Communication Network"]
plot_type = "network"
legend-position = "none"
theme = "theme_blank"
theme_args = {add_coord = false}
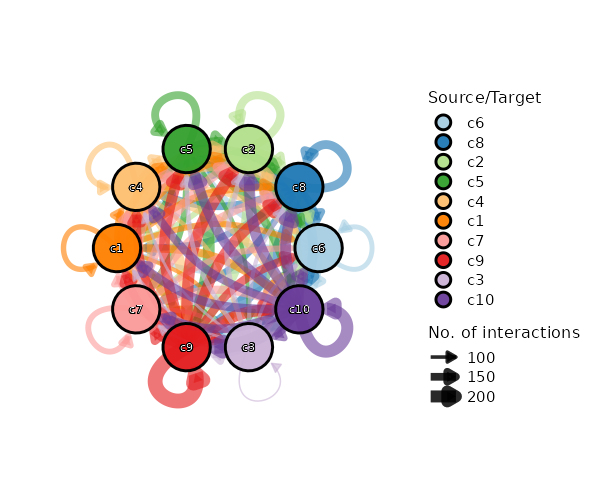 {: width="80%"}
{: width="80%"}
Circos Plot
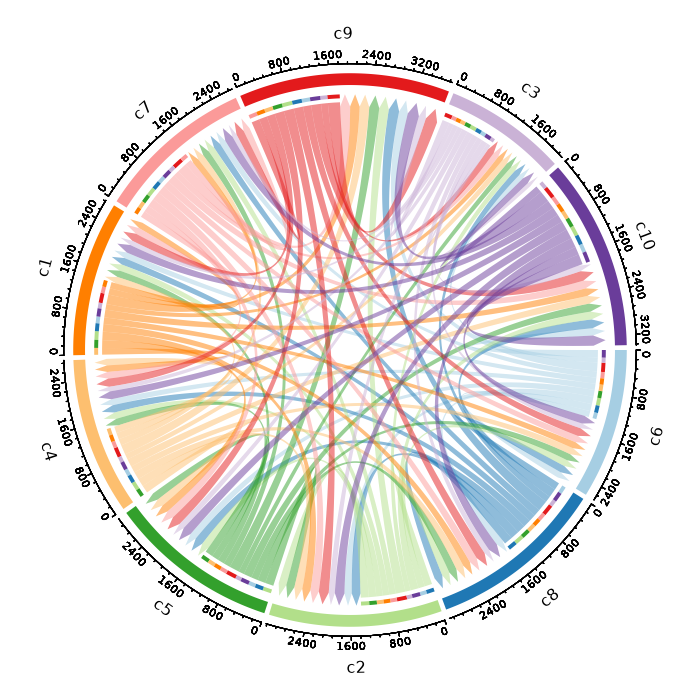 {: width="80%"}
{: width="80%"}
Heatmap Plot
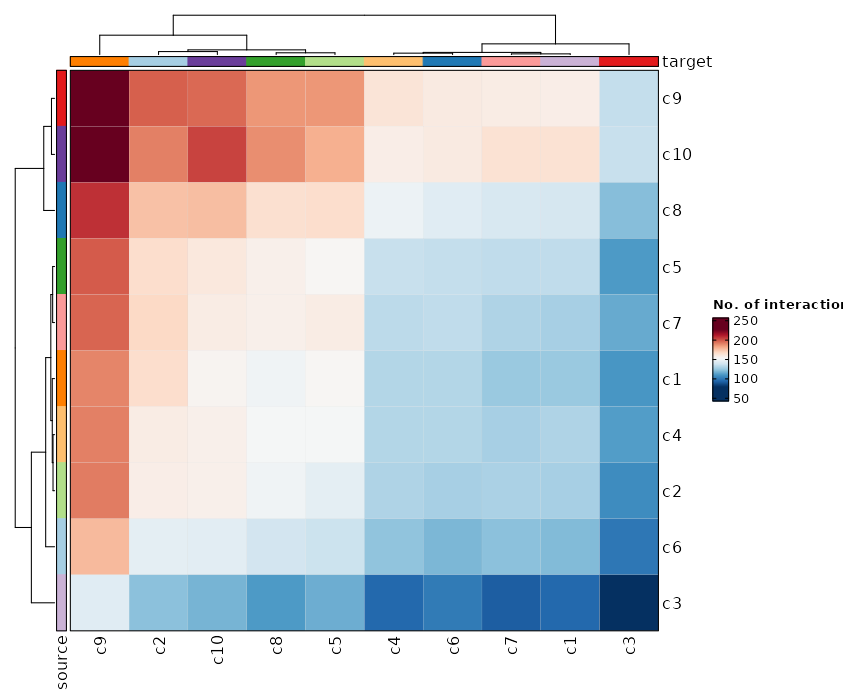 {: width="80%"}
{: width="80%"}
Cell-Cell Communication Interaction (Box Plot)
[CellCellCommunicationPlots.envs.cases."Cell-Cell Communication Interaction (Box Plot)"]
plot_type = "box"
x_text_angle = 90
method = "interaction"
 {: width="80%"}
{: width="80%"}
cccfile— The output file fromCellCellCommunication
outdir— The output directory for the plots.
cases(type=json) — The cases for the plots.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the arguments for the plots. The arguments include the ones inherited fromenvs. You can have a specialplot_type"table"to generate a table for the ccc data to save as a text file and show in the report. If no cases are given, a default case will be used, with the keyCell-Cell Communication.descr— The description of the plot.devpars(ns) — The parameters for the plot.- - res (type=int): The resolution of the plot
- - height (type=int): The height of the plot
- - width (type=int): The width of the plot
magnitude— The column name in the data to use as the magnitude of thecommunication. By default, the second last column will be used. Seeli.mt.show_methods()for the available methods in LIANA. or https://liana-py.readthedocs.io/en/latest/notebooks/basic_usage.html#Tileplotmore_formats(type=list) — The additional formats to save the plots.specificity— The column name in the data to use as the specificity of the communication.By default, the last column will be used. If the method doesn't have a specificity, set it to None.subset— An expression to pass todplyr::filter()to subset the ccc data.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.ScVelo(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Velocity analysis for single-cell RNA-seq data
This process is implemented based on the Python package scvelo (v0.3.3).
Note that it doesn't work with numpy>=2.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
sobjfile— The seurat object file in RDS or h5seurat format or AnnData file.
outfile— The output object with the velocity embeddings and information.In either RDS, h5seurat or h5ad format, depending on theenvs.outtype. There will be also plots generated in the output directory (parent directory ofoutfile). Note that these plots will not be used in the report, but can be used as supplementary information for the velocity analysis. To visualize the velocity embeddings, you can use theSeuratClusterStatsprocess withv_reductionprovided to one of theenvs.dimplots.
calculate_velocity_genes(flag) — Whether to calculate the velocity genes.denoise(flag) — Whether to denoise the data.denoise_topn(type=int) — Number of genes with highest likelihood selected toinfer velocity directions.fitting_by(choice) — The mode to use for fitting the velocities.- - stochastic: Stochastic mode
- - deterministic: Deterministic mode
group_by— The column name in metadata to group the cells.Typically, this column should be the cluster id. If provided input is a Seurat object, the default identity will be used by default. Otherwise, it is recommended to provide this parameter. "seurat_clusters" will be used with a warning if the input is in AnnData format and this parameter is not provided.kinetics(flag) — Whether to compute the RNA velocity kinetics.kinetics_topn(type=int) — Number of genes with highest likelihood selected toinfer velocity directions.min_shared_counts(type=int) — Minimum number of counts(both unspliced and spliced) required for a gene.mode(type=list) — The mode to use for the velocity analysis.It should be a subset of['deterministic', 'stochastic', 'dynamical'], meaning that we can perform the velocity analysis in multiple modes.n_neighbors(type=int) — The number of neighbors to use for the velocity graph.n_pcs(type=int) — The number of PCs to use for the velocity graph.ncores(type=int) — Number of cores to use.outtype(choice) — The output file type.- - : The same as the input file type.
- - h5seurat: h5seurat file
- - h5ad: h5ad file
- - qs: qs/qs2 file
- - qs2: qs2 file
- - rds: RDS file
rscript— The path to the Rscript executable used to convert RDS file to AnnData.ifin.sobjfileis an RDS file, it will be converted to AnnData file (h5ad). You needSeurat,SeuratDiskanddigestinstalled.top_n(type=int) — The number of top features to plot.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.Slingshot(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Trajectory inference using Slingshot
This process is implemented based on the R package slingshot.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
sobjfile— The seurat object file in RDS or qs format.
outfile— The output object with the trajectory information.The lineages are stored in the metadata of the seurat object at columnsLineageX, where X is the lineage number. TheBranchIDcolumn contains the branch id for each cell. One can usescplotter::CellDimPlot(object, lineages = c("Lineage1", "Lineage2", ...))to visualize the trajectories.
align_start(flag) — Whether to align the starting pseudotime values at the maximum pseudotime.dims(type=auto) — The dimensions to use for the analysis.A list or a string with comma separated values. Consecutive numbers can be specified with a colon (:) or a dash (-).end— The ending group for the Slingshot analysis.group_by— The column name in metadata to group the cells.Typically, this column should be the cluster id. Default is the default identity of the seurat object.prefix— The prefix to add to the column names of the resulting pseudotime variable.reduction— The nonlinear reduction to use for the trajectory analysis.reverse(flag) — Logical value indicating whether to reverse the pseudotime variable.seed(type=int) — The seed for the random number generator.start— The starting group for the Slingshot analysis.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.LoomTo10X(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Convert Loom file to 10X format
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
loomfile— The Loom file
outdir— The output directory for the 10X format files,including thematrix.mtx.gz,barcodes.tsv.gzandfeatures.tsv.gzfiles.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.PseudoBulkDEG(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Pseduo-bulk differential gene expression analysis
This process performs differential gene expression analysis, instead of on single-cell level, on the pseudo-bulk data, aggregated from the single-cell data.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
sobjfile— The seurat object file in RDS or qs/qs2 format.
outdir— The output containing the results of the differential gene expressionanalysis.
aggregate_by— The column names in metadata to aggregate the cells.allenrich_plots(type=json) — Cases of the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromallenrich_plots_defaults. The cases underenvs.casescan inherit this options.allenrich_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/EnrichmentPlot.html.
allmarker_plots(type=json) — All marker plot cases.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromallmarker_plots_defaults.allmarker_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots for all markers whenident_1is not specified.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/FeatureStatPlot.html.
Available types areviolin,box,bar,ridge,dim,heatmapanddot. - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - - order_by: an expression to order the markers, passed by
dplyr::arrange(). - - genes: The number of top genes to show or an expression passed to
dplyr::filter()to filter the genes. - -
: Other arguments passed to scplotter::FeatureStatPlot().
- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
assay— The assay to pull and aggregate the data.cache(type=auto) — Where to cache the results.IfTrue, cache tooutdirof the job. IfFalse, don't cache. Otherwise, specify the directory to cache to.cases(type=json) — The cases for the analysis.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the arguments for the analysis. The arguments include the ones inherited fromenvs. If no cases are specified, a default case will be added with the nameDEG Analysisand the default values specified above.dbs(list) — The databases to use for enrichment analysis.You can use built-in dbs inenrichit, or provide your own gmt files. See also https://pwwang.github.io/enrichit/reference/FetchGMT.html. The built-in dbs include:- * "BioCarta" or "BioCarta_2016"
- * "GO_Biological_Process" or "GO_Biological_Process_2025"
- * "GO_Cellular_Component" or "GO_Cellular_Component_2025"
- * "GO_Molecular_Function" or "GO_Molecular_Function_2025"
- * "KEGG", "KEGG_Human", "KEGG_2021", or "KEGG_2021_Human"
- * "Hallmark", "MSigDB_Hallmark", or "MSigDB_Hallmark_2020"
- * "Reactome", "Reactome_Pathways", or "Reactome_Pathways_2024"
- * "WikiPathways", "WikiPathways_2024", "WikiPathways_Human", or "WikiPathways_2024_Human"
each— The column name in metadata to separate the cells into different cases.When specified, the case will be expanded to multiple cases for each value in the column.enrich_plots(type=json) — Cases of the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromenrich_plots_defaults. The cases underenvs.casescan inherit this options.enrich_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots to generate for the enrichment analysis.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/EnrichmentPlot.html.
Available types arebar,dot,lollipop,network,enrichmapandwordcloud. - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/EnrichmentPlot.htmll.
- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
enrich_style(choice) — The style of the enrichment analysis.- - enrichr: Use
enrichr-style for the enrichment analysis. - - clusterProfiler: Use
clusterProfiler-style for the enrichment analysis.
- - enrichr: Use
error(flag) — Error out if no/not enough markers are found or no pathways are enriched.IfFalse, empty results will be returned.group_by— The column name in metadata to group the cells.ident_1— The first identity to compare.ident_2— The second identity to compare.If not specified, the rest of the identities will be compared withident_1.layer— The layer to pull and aggregate the data.marker_plots(type=json) — Cases of the plots to generate for the markers.Plot cases. The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited frommarker_plots_defaults. The cases underenvs.casescan inherit this options.marker_plots_defaults(ns) — Default options for the plots to generate for the markers.- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/FeatureStatPlot.html.
Available types areviolin,box,bar,ridge,dim,heatmapanddot.
There are two additional types available -volcano_pctandvolcano_log2fc. - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - - order_by: an expression to order the markers, passed by
dplyr::arrange(). - - genes: The number of top genes to show or an expression passed to
dplyr::filter()to filter the genes. - -
: Other arguments passed to scplotter::FeatureStatPlot().
Ifplot_typeisvolcano_pctorvolcano_log2fc, they will be passed to
scplotter::VolcanoPlot().
- - plot_type: The type of the plot.
mutaters(type=json) — Mutaters to mutate the metadata of theseurat object. Keys are the new column names and values are the expressions to mutate the columns. These new columns can be used to define your cases. You can also use the clone selectors to select the TCR clones/clusters. See https://pwwang.github.io/scplotter/reference/clone_selectors.html.ncores(type=int) — Number of cores to use for parallelization.overlaps(type=json) — Cases for investigating the overlapping of significant markers between different cases or comparisons.The keys are the names of the cases and the values are the dicts inherited fromoverlaps_defaults. There are two situations that we can perform overlaps: 1. Ifident_1is not specified, the overlaps can be performed between different comparisons. 2. Ifeachis specified, the overlaps can be performed between different cases, where in each case,ident_1must be specified.overlaps_defaults(ns) — Default options for investigating the overlapping of significant markers between different cases or comparisons.This means eitherident_1should be empty, so that they can be expanded to multiple comparisons.- - sigmarkers: The expression to filter the significant markers for each case.
If not provided,envs.sigmarkerswill be used. - - plot_type (choice): The type of the plot to generate for the overlaps.
- venn: Useplotthis::VennDiagram().
- upset: Useplotthis::UpsetPlot(). - - more_formats (type=list): The extra formats to save the plot in.
- - save_code (flag): Whether to save the code to generate the plot.
- - devpars (ns): The device parameters for the plots.
- res (type=int): The resolution of the plots.
- height (type=int): The height of the plots.
- width (type=int): The width of the plots. - -
: More arguments pased to plotthis::VennDiagram()
(https://pwwang.github.io/plotthis/reference/venndiagram1.html)
orplotthis::UpsetPlot()
(https://pwwang.github.io/plotthis/reference/upsetplot1.html)
- - sigmarkers: The expression to filter the significant markers for each case.
paired_by— The column name in metadata to mark the paired samples.For example, subject. If specified, the paired test will be performed.plots(type=json) — The parameters for the plots.The keys are the names of the plots and the values are the parameters for the plots. The parameters will override the defaults inplots_defaults. If not specified, no plots will be generated.plots_defaults(ns) — The default parameters for the plots.- -
: Parameters passed to biopipen.utils::VizBulkDEGs().
See: https://pwwang.github.io/biopipen.utils.R/reference/VizBulkDEGs.html
- -
sigmarkers— An expression passed todplyr::filter()to filter thesignificant markers for enrichment analysis. The default isp_val_adj < 0.05. Iftool = 'DESeq2', the variables that can be used for filtering are:baseMean,log2FC,lfcSE,stat,p_val,p_val_adj. Iftool = 'edgeR', the variables that can be used for filtering are:logCPM,log2FC,LR,p_val,p_val_adj.subset— An expression in string to subset the cells.tool(choice) — The method to use for the differential expression analysis.- - DESeq2: Use DESeq2 for the analysis.
- - edgeR: Use edgeR for the analysis.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.CellSNPLite(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Genotyping bi-allelic SNPs on single cells using cellsnp-lite.
The output from cellsnp-lite can be directly used for downstream analysis such as -
- Donor deconvolution in multiplexed single-cell RNA-seq data (e.g., with vireo).
- Allele-specific CNV analysis in single-cell or spatial transcriptomics data (e.g., with Numbat, XClone, or CalicoST).
- Clonal substructure discovery using single cell mitochondrial variants (e.g., with MQuad).
Here we only support model 1a/2a in cellsnp-lite, which is designed for a single bam file as input.
For model 1b/2b, which is designed for multiple bam files as input (e.g., one per cell), you can still
run with this process, but only one bam file is allowed.
See https://github.com/single-cell-genetics/cellsnp-lite for more details about cellsnp-lite.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
crdir— The cellranger output directory or the directory containingthe bam file and barcode file. It should contain theouts/possorted_genome_bam.bamfile and theouts/filtered_feature_bc_matrix/barcodes.tsv.gzfile.
outdir— The output directory for cellsnp-lite results.
genotype(flag) — Whether to perform genotyping.IfFalse, only the allele counts will be computed.gzip(flag) — Whether to gzip the output files.ncores(type=int) — The number of cores to use.Will pass to-poption in cellsnp-lite.regionsVCF— A vcf file listing all candidate SNPs, for fetch each variants.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.MQuad(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Clonal substructure discovery using single cell mitochondrial variants with MQuad.
MQuad uses a Mixture Model for Mitochondrial Mutation detection in single-cell omics data.
MQuad is a tool that detects mitochondrial mutations that are informative for clonal substructure inference. It uses a binomial mixture model to assess the heteroplasmy of mtDNA variants among background noise.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
cellsnpout— The output directory fromCellSNPLiteprocess, which should containAD and DP sparse matrices (.mtx) or the vcf file.
outdir— The output directory for MQuad results.
ncores(type=int) — The number of cores to use.It will be passed to--nprocoption in MQuad.seed(type=int) — The seed for the random number generator.It will be passed to--randSeedoption in MQuad.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.MQuadMerge(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Merge multiple MQuad results for multiple samples.
We will merge the passed_ad.mtx, passed_dp.mtx and passed_variant_names.txt files from multiple samples
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
mquaddirs— The output directories fromMQuadprocess for multiple samples.
outdir— The output directory for merged MQuad results.This can be later used as input toVireoSNPprocess.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger
biopipen.ns.scrna.VireoSNP(*args, **kwds) → Proc
Demultiplexing of single-cell RNA-seq data using vireoSNP.
VireoSNP is a Bayesian method for demultiplexing pooled single-cell RNA-seq data using natural genetic variations (SNPs) without requiring genotype reference.
Refers to https://github.com/single-cell-genetics/vireo/blob/master/examples/vireoSNP_clones.ipynb for more details.
cache— Should we detect whether the jobs are cached?desc— The description of the process. Will use the summary fromthe docstring by default.dirsig— When checking the signature for caching, whether should we walkthrough the content of the directory? This is sometimes time-consuming if the directory is big.envs— The arguments that are job-independent, useful for common optionsacross jobs.envs_depth— How deep to update the envs when subclassed.error_strategy— How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
export— When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processesforks— How many jobs to run simultaneously?input— The keys for the input channelinput_data— The input data (will be computed for dependent processes)lang— The language for the script to run. Should be the path to theinterpreter iflangis not in$PATH.name— The name of the process. Will use the class name by default.nexts— Computed fromrequiresto build the process relationshipsnum_retries— How many times to retry to jobs once error occursorder— The execution order for this process. The bigger the numberis, the later the process will be executed. Default: 0. Note that the dependent processes will always be executed first. This doesn't work for start processes either, whose orders are determined byPipen.set_starts()output— The output keys for the output channel(the data will be computed)output_data— The output data (to pass to the next processes)plugin_opts— Options for process-level pluginsrequires— The dependency processesscheduler— The scheduler to run the jobsscheduler_opts— The options for the schedulerscript— The script template for the processsubmission_batch— How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.The program entrance for some schedulers may take too much resources when submitting a job or checking the job status. So we may use a smaller number here to limit the simultaneous submissions.template— Define the template engine to use.This could be either a template engine or a dict with keyengineindicating the template engine and the rest the arguments passed to the constructor of thepipen.template.Templateobject. The template engine could be either the name of the engine, currently jinja2 and liquidpy are supported, or a subclass ofpipen.template.Template. You can subclasspipen.template.Templateto use your own template engine.
cellsnpout— The output directory fromCellSNPLiteprocess, which shouldcontain AD and DP sparse matrices (.mtx) or the vcf file. To investigate the clonal substructure using mitochondrial variants, runMQuadfirst to select the informative variants, and then use the filtered vcf file from MQuad as input to this process.
outdir— The output directory for vireoSNP results.
max_iter(type=int) — The maximum number of iterations to perform.min_iter(type=int) — The minimum number of iterations to perform.n_clones(type=auto) — The number of clones in the pooled single-cell RNA-seq data.(Refered asn_donorin vireoSNP documentation.) If a 2-element list of provided, we will try to estimate the best number of clones between the two values using the elbow plot method.n_init(type=int) — The number of random initializations to perform.ncores(type=int) — The number of cores to use for model fitting fordifferent number of clones.seed(type=int) — The seed for the random number generator.
__init_subclass__()— Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship </>from_proc(proc,name,desc,envs,envs_depth,cache,export,error_strategy,num_retries,forks,input_data,order,plugin_opts,requires,scheduler,scheduler_opts,submission_batch)(Type) — Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself</>gc()— GC process for the process to save memory after it's done</>log(level,msg,*args,logger)— Log message for the process</>run()— Init all other properties and jobs</>
pipen.proc.ProcMeta(name, bases, namespace, **kwargs)
Meta class for Proc
__call__(cls,*args,**kwds)(Proc) — Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons</>__instancecheck__(cls,instance)— Override for isinstance(instance, cls).</>__repr__(cls)(str) — Representation for the Proc subclasses</>__subclasscheck__(cls,subclass)— Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).</>register(cls,subclass)— Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.</>
register(cls, subclass)Register a virtual subclass of an ABC.
Returns the subclass, to allow usage as a class decorator.
__instancecheck__(cls, instance)Override for isinstance(instance, cls).
__subclasscheck__(cls, subclass)Override for issubclass(subclass, cls).
__repr__(cls) → strRepresentation for the Proc subclasses
__call__(cls, *args, **kwds)Make sure Proc subclasses are singletons
*args(Any) — and**kwds(Any) — Arguments for the constructor
The Proc instance
from_proc(proc, name=None, desc=None, envs=None, envs_depth=None, cache=None, export=None, error_strategy=None, num_retries=None, forks=None, input_data=None, order=None, plugin_opts=None, requires=None, scheduler=None, scheduler_opts=None, submission_batch=None)
Create a subclass of Proc using another Proc subclass or Proc itself
proc(Type) — The Proc subclassname(str, optional) — The new name of the processdesc(str, optional) — The new description of the processenvs(Mapping, optional) — The arguments of the process, will overwrite parent oneThe items that are specified will be inheritedenvs_depth(int, optional) — How deep to update the envs when subclassed.cache(bool, optional) — Whether we should check the cache for the jobsexport(bool, optional) — When True, the results will be exported to<pipeline.outdir>Defaults to None, meaning only end processes will export. You can set it to True/False to enable or disable exporting for processeserror_strategy(str, optional) — How to deal with the errors- - retry, ignore, halt
- - halt to halt the whole pipeline, no submitting new jobs
- - terminate to just terminate the job itself
num_retries(int, optional) — How many times to retry to jobs once error occursforks(int, optional) — New forks for the new processinput_data(Any, optional) — The input data for the process. Only when this processis a start processorder(int, optional) — The order to execute the new processplugin_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new plugin options, unspecified items will beinherited.requires(Sequence, optional) — The required processes for the new processscheduler(str, optional) — The new shedular to run the new processscheduler_opts(Mapping, optional) — The new scheduler options, unspecified items willbe inherited.submission_batch(int, optional) — How many jobs to be submited simultaneously.
The new process class
__init_subclass__()
Do the requirements inferring since we need them to build up theprocess relationship
run()
Init all other properties and jobs
gc()
GC process for the process to save memory after it's done
log(level, msg, *args, logger=<LoggerAdapter pipen.core (WARNING)>)
Log message for the process
level(int | str) — The log level of the recordmsg(str) — The message to log*args— The arguments to format the messagelogger(LoggerAdapter, optional) — The logging logger