"""Provides processes for statistics."""
from ..core.proc import Proc
from ..core.config import config
class ChowTest(Proc):DOCS
"""Massive Chow tests.
See Also https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chow_test
Input:
infile: The input data file. The rows are samples and the columns are
features. It must be tab-delimited.
```
Sample F1 F2 F3 ... Fn
S1 1.2 3.4 5.6 7.8
S2 2.3 4.5 6.7 8.9
...
Sm 5.6 7.8 9.0 1.2
```
groupfile: The group file. The rows are the samples and the columns
are the groupings. It must be tab-delimited.
```
Sample G1 G2 G3 ... Gk
S1 0 1 0 0
S2 2 1 0 NA # exclude this sample
...
Sm 1 0 0 0
```
fmlfile: The formula file. The first column is grouping and the
second column is the formula. It must be tab-delimited.
```
Group Formula ... # Other columns to be added to outfile
G1 Fn ~ F1 + Fx + Fy # Fx, Fy could be covariates
G1 Fn ~ F2 + Fx + Fy
...
Gk Fn ~ F3 + Fx + Fy
```
Output:
outfile: The output file. It is a tab-delimited file with the first
column as the grouping and the second column as the p-value.
```
Group Formula ... Pooled Groups SSR SumSSR Fstat Pval Padj
G1 Fn ~ F1 0.123 2 1 0.123 0.123 0.123 0.123
G1 Fn ~ F2 0.123 2 1 0.123 0.123 0.123 0.123
...
Gk Fn ~ F3 0.123 2 1 0.123 0.123 0.123 0.123
```
Envs:
padj (choice): The method for p-value adjustment.
- none: No p-value adjustment (no Padj column in outfile).
- holm: Holm-Bonferroni method.
- hochberg: Hochberg method.
- hommel: Hommel method.
- bonferroni: Bonferroni method.
- BH: Benjamini-Hochberg method.
- BY: Benjamini-Yekutieli method.
- fdr: FDR correction method.
transpose_input (flag): Whether to transpose the input file.
transpose_group (flag): Whether to transpose the group file.
"""
input = "infile:file, groupfile:file, fmlfile:file"
output = "outfile:file:{{in.infile | stem}}.chowtest.txt"
lang = config.lang.rscript
envs = {
"padj": "none",
"transpose_input": False,
"transpose_group": False,
}
script = "file://../scripts/stats/ChowTest.R"
class Mediation(Proc):DOCS
"""Mediation analysis.
The flowchart of mediation analysis:
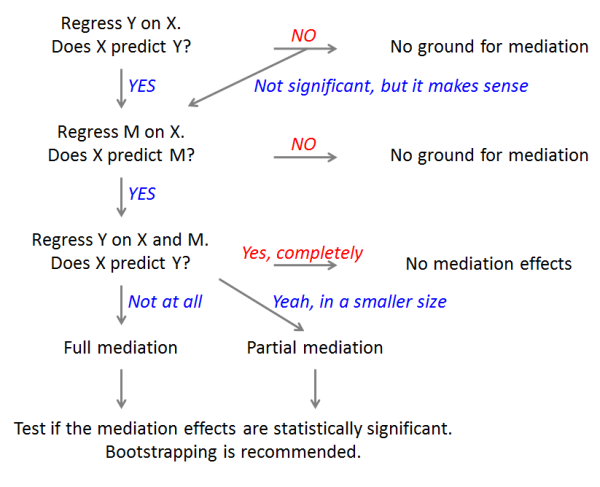
Reference:
- <https://library.virginia.edu/data/articles/introduction-to-mediation-analysis>
- <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mediation_(statistics)>
- <https://tilburgsciencehub.com/topics/analyze/regression/linear-regression/mediation-analysis/>
- <https://ademos.people.uic.edu/Chapter14.html>
Input:
infile: The input data file. The rows are samples and the columns are
features. It must be tab-delimited.
```
Sample F1 F2 F3 ... Fn
S1 1.2 3.4 5.6 7.8
S2 2.3 4.5 6.7 8.9
...
Sm 5.6 7.8 9.0 1.2
```
fmlfile: The formula file.
```
Case M Y X Cov Model_M Model_Y
Case1 F1 F2 F3 F4,F5 glm lm
...
```
Where Y is the outcome variable, X is the predictor variable, M is the
mediator variable, and Case is the case name. Model_M and Model_Y are the
models for M and Y, respectively.
`envs.cases` will be ignored if this is provided.
Output:
outfile: The output file.
Columns to help understand the results:
Total Effect: a total effect of X on Y (without M) (`Y ~ X`).
ADE: A Direct Effect of X on Y after taking into account a mediation effect of M (`Y ~ X + M`).
ACME: The Mediation Effect, the total effect minus the direct effect,
which equals to a product of a coefficient of X in the second step and a coefficient of M in the last step.
The goal of mediation analysis is to obtain this indirect effect and see if it's statistically significant.
Envs:
ncores (type=int): Number of cores to use for parallelization for cases.
sims (type=int): Number of Monte Carlo draws for nonparametric bootstrap or quasi-Bayesian approximation.
Will be passed to `mediation::mediate` function.
args (ns): Other arguments passed to `mediation::mediate` function.
- <more>: More arguments passed to `mediation::mediate` function.
See: <https://rdrr.io/cran/mediation/man/mediate.html>
padj (choice): The method for (ACME) p-value adjustment.
- none: No p-value adjustment (no Padj column in outfile).
- holm: Holm-Bonferroni method.
- hochberg: Hochberg method.
- hommel: Hommel method.
- bonferroni: Bonferroni method.
- BH: Benjamini-Hochberg method.
- BY: Benjamini-Yekutieli method.
- fdr: FDR correction method.
cases (type=json): The cases for mediation analysis.
Ignored if `in.fmlfile` is provided.
A json/dict with case names as keys and values as a dict of M, Y, X, Cov, Model_M, Model_Y.
For example:
```json
{
"Case1": {
"M": "F1",
"Y": "F2",
"X": "F3",
"Cov": "F4,F5",
"Model_M": "glm",
"Model_Y": "lm"
},
...
}
```
transpose_input (flag): Whether to transpose the input file.
""" # noqa: E501
input = "infile:file, fmlfile:file"
output = "outfile:file:{{in.infile | stem}}.mediation.txt"
lang = config.lang.rscript
envs = {
"ncores": config.misc.ncores,
"sims": 1000,
"args": {},
"padj": "none",
"cases": {},
"transpose_input": False,
}
script = "file://../scripts/stats/Mediation.R"
class LiquidAssoc(Proc):DOCS
"""Liquid association tests.
See Also https://github.com/gundt/fastLiquidAssociation
Requires https://github.com/pwwang/fastLiquidAssociation
Input:
infile: The input data file. The rows are samples and the columns are
features. It must be tab-delimited.
```
Sample F1 F2 F3 ... Fn
S1 1.2 3.4 5.6 7.8
S2 2.3 4.5 6.7 8.9
...
Sm 5.6 7.8 9.0 1.2
```
The features (columns) will be tested pairwise, which will be the X and
Y columns in the result of `fastMLA`
covfile: The covariate file. The rows are the samples and the columns
are the covariates. It must be tab-delimited.
If provided, the data in `in.infile` will be adjusted by covariates by
regressing out the covariates and the residuals will be used for
liquid association tests.
groupfile: The group file. The rows are the samples and the columns
are the groupings. It must be tab-delimited.
```
Sample G1 G2 G3 ... Gk
S1 0 1 0 0
S2 2 1 0 NA # exclude this sample
...
Sm 1 0 0 0
```
This will be served as the Z column in the result of `fastMLA`
This can be omitted. If so, `envs.nvec` should be specified, which is
to select column from `in.infile` as Z.
fmlfile: The formula file. The 3 columns are X3, X12 and X21. The results
will be filtered based on the formula. It must be tab-delimited without
header.
Output:
outfile: The output file.
```
X12 X21 X3 rhodiff MLA value estimates san.se wald Pval model
C38 C46 C5 0.87 0.32 0.67 0.20 10.87 0 F
C46 C38 C5 0.87 0.32 0.67 0.20 10.87 0 F
C27 C39 C4 0.94 0.34 1.22 0.38 10.03 0 F
```
Envs:
nvec: The column index (1-based) of Z in `in.infile`, if `in.groupfile` is
omitted. You can specify multiple columns by comma-seperated values, or
a range of columns by `-`. For example, `1,3,5-7,9`. It also supports
column names. For example, `F1,F3`. `-` is not supported for column
names.
x: Similar as `nvec`, but limit X group to given features.
The rest of features (other than X and Z) in `in.infile` will
be used as Y.
The features in `in.infile` will still be tested pairwise, but only
features in X and Y will be kept.
topn (type=int): Number of results to return by `fastMLA`, ordered from
highest `|MLA|` value descending.
The default of the package is 2000, but here we set to 1e6 to return as
many results as possible (also good to do pvalue adjustment).
rvalue (type=float): Tolerance value for LA approximation. Lower values of
rvalue will cause a more thorough search, but take longer.
cut (type=int): Value passed to the GLA function to create buckets
(equal to number of buckets+1). Values placing between 15-30 samples per
bucket are optimal. Must be a positive integer>1. By default,
`max(ceiling(nrow(data)/22), 4)` is used.
ncores (type=int): Number of cores to use for parallelization.
padj (choice): The method for p-value adjustment.
- none: No p-value adjustment (no Padj column in outfile).
- holm: Holm-Bonferroni method.
- hochberg: Hochberg method.
- hommel: Hommel method.
- bonferroni: Bonferroni method.
- BH: Benjamini-Hochberg method.
- BY: Benjamini-Yekutieli method.
- fdr: FDR correction method.
transpose_input (flag): Whether to transpose the input file.
transpose_group (flag): Whether to transpose the group file.
transpose_cov (flag): Whether to transpose the covariate file.
xyz_names: The names of X12, X21 and X3 in the final output file. Separated
by comma. For example, `X12,X21,X3`.
"""
input = "infile:file, covfile:file, groupfile:file, fmlfile:file"
output = "outfile:file:{{in.infile | stem}}.liquidassoc.txt"
lang = config.lang.rscript
envs = {
"nvec": None,
"x": None,
"topn": 1e6,
"rvalue": 0.5,
"cut": 20,
"ncores": config.misc.ncores,
"padj": "none",
"transpose_input": False,
"transpose_group": False,
"transpose_cov": False,
"xyz_names": None,
}
script = "file://../scripts/stats/LiquidAssoc.R"
class DiffCoexpr(Proc):DOCS
"""Differential co-expression analysis.
See also <https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2105-11-497>
and <https://github.com/DavisLaboratory/dcanr/blob/8958d61788937eef3b7e2b4118651cbd7af7469d/R/inference_methods.R#L199>.
Input:
infile: The input data file. The rows are samples and the columns are
features. It must be tab-delimited.
```
Sample F1 F2 F3 ... Fn
S1 1.2 3.4 5.6 7.8
S2 2.3 4.5 6.7 8.9
...
Sm 5.6 7.8 9.0 1.2
```
groupfile: The group file. The rows are the samples and the columns
are the groupings. It must be tab-delimited.
```
Sample G1 G2 G3 ... Gk
S1 0 1 0 0
S2 2 1 0 NA # exclude this sample
...
Sm 1 0 0 0
```
Output:
outfile: The output file. It is a tab-delimited file with the first
column as the feature pair and the second column as the p-value.
```
Group Feature1 Feature2 Pval Padj
G1 F1 F2 0.123 0.123
G1 F1 F3 0.123 0.123
...
```
Envs:
method (choice): The method used to calculate the differential
co-expression.
- pearson: Pearson correlation.
- spearman: Spearman correlation.
beta: The beta value for the differential co-expression analysis.
padj (choice): The method for p-value adjustment.
- none: No p-value adjustment (no Padj column in outfile).
- holm: Holm-Bonferroni method.
- hochberg: Hochberg method.
- hommel: Hommel method.
- bonferroni: Bonferroni method.
- BH: Benjamini-Hochberg method.
- BY: Benjamini-Yekutieli method.
- fdr: FDR correction method.
perm_batch (type=int): The number of permutations to run in each batch
seed (type=int): The seed for random number generation
ncores (type=int): The number of cores to use for parallelization
transpose_input (flag): Whether to transpose the input file.
transpose_group (flag): Whether to transpose the group file.
""" # noqa: E501
input = "infile:file, groupfile:file"
output = "outfile:file:{{in.infile | stem}}.diffcoexpr.txt"
lang = config.lang.rscript
envs = {
"method": "pearson",
"beta": 6,
"padj": "none",
"perm_batch": 20,
"seed": 8525,
"ncores": config.misc.ncores,
"transpose_input": False,
"transpose_group": False,
}
script = "file://../scripts/stats/DiffCoexpr.R"
class MetaPvalue(Proc):DOCS
"""Calulation of meta p-values.
If there is only one input file, only the p-value adjustment will be performed.
Input:
infiles: The input files. Each file is a tab-delimited file with multiple
columns. There should be ID column(s) to match the rows in other files and
p-value column(s) to be combined. The records will be full-joined by ID.
When only one file is provided, only the pvalue adjustment will be
performed when `envs.padj` is not `none`, otherwise the input file will
be copied to `out.outfile`.
Output:
outfile: The output file. It is a tab-delimited file with the first column as
the ID and the second column as the combined p-value.
```
ID ID1 ... Pval Padj
a x ... 0.123 0.123
b y ... 0.123 0.123
...
```
Envs:
id_cols: The column names used in all `in.infiles` as ID columns. Multiple
columns can be specified by comma-seperated values. For example, `ID1,ID2`,
where `ID1` is the ID column in the first file and `ID2` is the ID column
in the second file.
If `id_exprs` is specified, this should be a single column name for the new
ID column in each `in.infiles` and the final `out.outfile`.
id_exprs: The R expressions for each `in.infiles` to get ID column(s).
pval_cols: The column names used in all `in.infiles` as p-value columns.
Different columns can be specified by comma-seperated values for each
`in.infiles`. For example, `Pval1,Pval2`.
method (choice): The method used to calculate the meta-pvalue.
- fisher: Fisher's method.
- sumlog: Sum of logarithms (same as Fisher's method)
- logitp: Logit method.
- sumz: Sum of z method (Stouffer's method).
- meanz: Mean of z method.
- meanp: Mean of p method.
- invt: Inverse t method.
- sump: Sum of p method (Edgington's method).
- votep: Vote counting method.
- wilkinsonp: Wilkinson's method.
- invchisq: Inverse chi-square method.
keep_single (flag): Whether to keep the original p-value when there is only one
p-value.
na: The method to handle NA values. -1 to skip the record. Otherwise NA
will be replaced by the given value.
padj (choice): The method for p-value adjustment.
- none: No p-value adjustment (no Padj column in outfile).
- holm: Holm-Bonferroni method.
- hochberg: Hochberg method.
- hommel: Hommel method.
- bonferroni: Bonferroni method.
- BH: Benjamini-Hochberg method.
- BY: Benjamini-Yekutieli method.
- fdr: FDR correction method.
"""
input = "infiles:files"
output = "outfile:file:{{in.infiles | first | stem}}.metapval.txt"
lang = config.lang.rscript
envs = {
"id_cols": None,
"id_exprs": None,
"pval_cols": None,
"method": "fisher",
"na": -1,
"keep_single": True,
"padj": "none",
}
script = "file://../scripts/stats/MetaPvalue.R"
class MetaPvalue1(Proc):DOCS
"""Calulation of meta p-values.
Unlike `MetaPvalue`, this process only accepts one input file.
The p-values will be grouped by the ID columns and combined by the selected method.
Input:
infile: The input file.
The file is a tab-delimited file with multiple
columns. There should be ID column(s) to group the rows where
p-value column(s) to be combined.
Output:
outfile: The output file. It is a tab-delimited file with the first column as
the ID and the second column as the combined p-value.
```
ID ID1 ... Pval Padj
a x ... 0.123 0.123
b y ... 0.123 0.123
...
```
Envs:
id_cols: The column names used in `in.infile` as ID columns. Multiple
columns can be specified by comma-seperated values. For example, `ID1,ID2`.
pval_col: The column name used in `in.infile` as p-value column.
method (choice): The method used to calculate the meta-pvalue.
- fisher: Fisher's method.
- sumlog: Sum of logarithms (same as Fisher's method)
- logitp: Logit method.
- sumz: Sum of z method (Stouffer's method).
- meanz: Mean of z method.
- meanp: Mean of p method.
- invt: Inverse t method.
- sump: Sum of p method (Edgington's method).
- votep: Vote counting method.
- wilkinsonp: Wilkinson's method.
- invchisq: Inverse chi-square method.
na: The method to handle NA values. -1 to skip the record. Otherwise NA
will be replaced by the given value.
keep_single (flag): Whether to keep the original p-value when there is only one
p-value.
padj (choice): The method for p-value adjustment.
- none: No p-value adjustment (no Padj column in outfile).
- holm: Holm-Bonferroni method.
- hochberg: Hochberg method.
- hommel: Hommel method.
- bonferroni: Bonferroni method.
- BH: Benjamini-Hochberg method.
- BY: Benjamini-Yekutieli method.
- fdr: FDR correction method.
"""
input = "infile:file"
output = "outfile:file:{{in.infile | stem}}.metapval.txt"
lang = config.lang.rscript
envs = {
"id_cols": None,
"pval_col": None,
"method": "fisher",
"na": -1,
"keep_single": True,
"padj": "none",
}
script = "file://../scripts/stats/MetaPvalue1.R"